Firewall Settings > QoS Mapping
755
SonicOS 5.8.1 Administrator Guide
The behavior of the 802.1p field within these tags can be controlled by Access Rules. The
default 802.1p Access Rule action of None will reset existing 802.1p tags to 0, unless otherwise
configured (see “Managing QoS Marking” section on page 760 for details).
Enabling 802.1p marking will allow the target interface to recognize incoming 802.1p tags
generated by 802.1p capable network devices, and will also allow the target interface to
generate 802.1p tags, as controlled by Access Rules. Frames that have 802.1p tags inserted
by SonicOS will bear VLAN ID 0.
802.1p tags will only be inserted according to Access Rules, so enabling 802.1p marking on an
interface will not, at its default setting, disrupt communications with 802.1p-incapable devices.
802.1p requires the specific support by the networking devices with which you wish to use this
method of prioritization. Many voice and video over IP devices provide support for 802.1p, but
the feature must be enabled. Check your equipment’s documentation for information on 802.1p
support if you are unsure. Similarly, many server and host network cards (NICs) have the ability
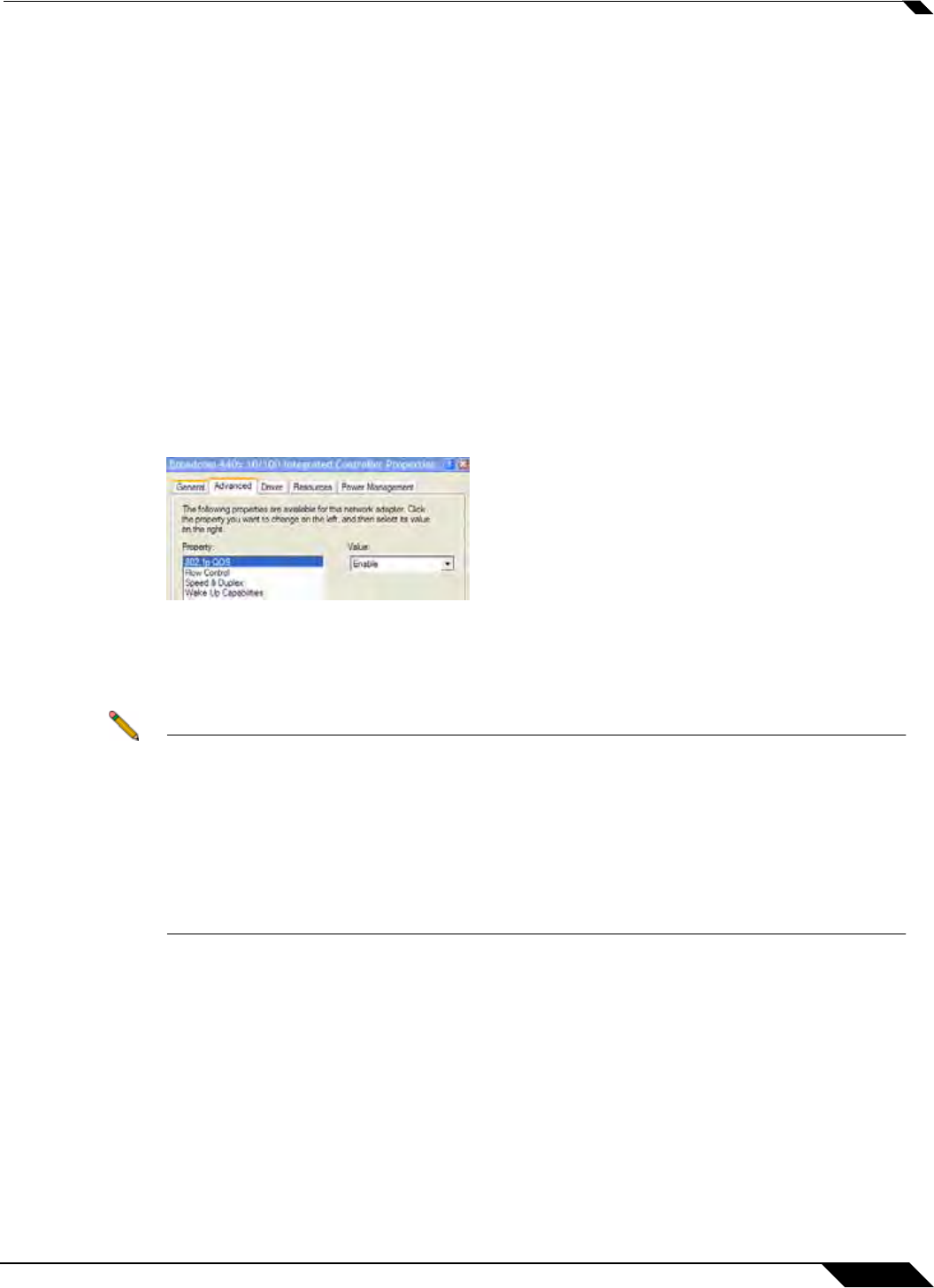
to support 802.1p, but the feature is usually disabled by default. On Win32 operating systems,
you can check for and configure 802.1p settings on the Advanced tab of the Properties page
of your network card. If your card supports 802.1p, it will list it as 802.1p QoS, 802.1p Support,
QoS Packet Tagging or something similar:
To process 802.1p tags, the feature must be present and enabled on the network interface. The
network interface will then be able to generate packets with 802.1p tags, as governed by QoS
capable applications. By default, general network communications will not have tags inserted
so as to maintain compatibility with 802.1p-incapable devices.
Note If your network interface does not support 802.1p, it will not be able to process 802.1p
tagged traffic, and will ignore it. Make certain when defining Access Rules to enable 802.1p
marking that the target devices are 802.1p capable.
It should also be noted that when performing a p
acket capture (for example, with the
diagnostic tool Ethereal) on 802.1p capable devices, some 802.1p capable devices will not
show the 802.1q header in the packet capture. Conversely, a packet capture performed on
an 802.1p-incapable device will almost invariably show the header, but the host will be
unable to process the packet.
Before moving on to “Managing QoS Marking” section on page 760, it is important to introduce
‘DSCP Marking’ because of the potential interdependency between the two marking methods,
as well as to explain why the interdependency exists.


















