System > Packet Monitor
142
SonicOS 5.8.1 Administrator Guide
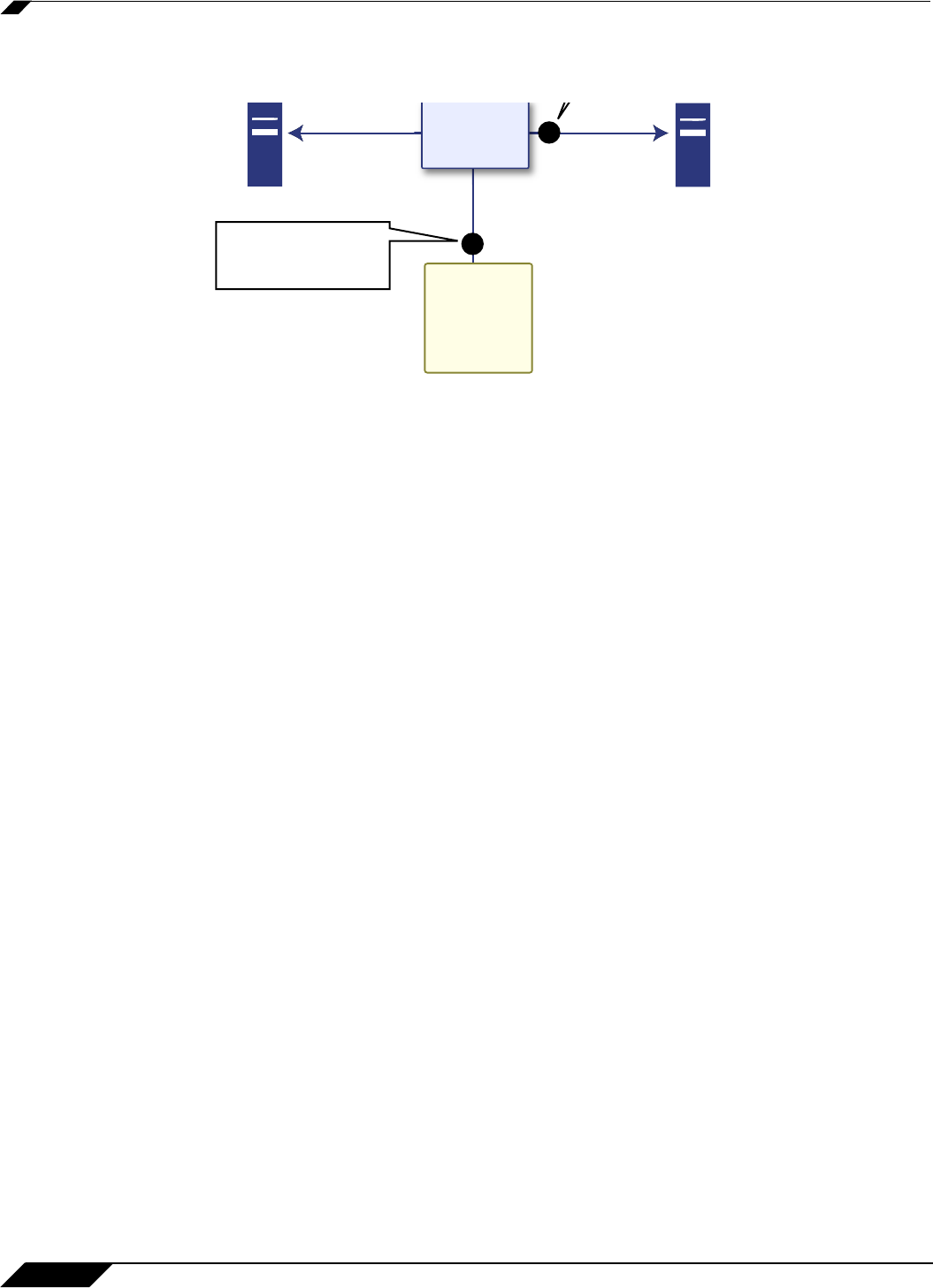
Refer to the figure below to see a high level view of the packet monitor subsystem. This shows
the different filters and how they are applied.
What is Packet Mirror?
Packet mirroring is the process of sending a copy of packets seen on one interface to another
interface or to a remote SonicWALL appliance.
There are two aspects of mirroring:
Classification – Refers to identifying a selected set of packets to be mirrored. Incoming and
outgoing packets to and from an interface are matched against a filter. If matched, the mirror
action is applied.
Action – Refers to sending a copy of the selected packets to a port or a remote destination.
Packets matching a classification filter are sent to one of the mirror destinations. A particular
mirror destination is part of the action identifier.
Supported Platforms for Packet Mirror
On all SonicWALL NSA Series appliances running SonicOS Enhanced 5.6 or higher, packet
mirroring is fully supported.
On SonicWALL TZ Series appliances running SonicOS Enhanced 5.6 or higher, packet
mirroring is partially supported, as follows:
• Local mirroring is not supported.
• Remote mirroring is supported for both sending and receiving mirrored packets.
How Does Packet Mirror Work?
Every classification filter is associated with an action identifier. Up to two action identifiers can
be defined, supporting two mirror destinations (a physical port on the same firewall and/or a
remote SonicWALL firewall). The action identifiers determine how a packet is mirrored. The
following types of action identifiers are supported:
• Send a copy to a physical port.
Remote FTP Server
Management Host
Capture Buffer
Packets
- Incoming
- Outgoing
- Generated
- Intermediate
Monitor filter is applied
before copying the packet
into the capture buffer.


















