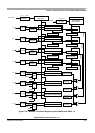
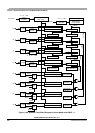
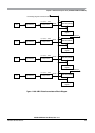
Chapter 11 Enhanced Capture Timer (S12MC9S12XDP51216B8CV2)
MC9S12XDP512 Data Sheet, Rev. 2.11
558 Freescale Semiconductor
11.4.1.6 Flag Clearing Mechanisms
The flags in the ECT can be cleared one of two ways:
1. Normal flag clearing mechanism (TFFCA = 0)
Any of the ECT flags can be cleared by writing a one to the flag.
2. Fast flag clearing mechanism (TFFCA = 1)
With the timer fast flag clear all (TFFCA) enabled, the ECT flags can only be cleared by accessing
the various registers associated with the ECT modes of operation as described below. The flags
cannot be cleared via the normal flag clearing mechanism. This fast flag clearing mechanism has
the advantage of eliminating the software overhead required by a separate clear sequence. Extra
care must be taken to avoid accidental flag clearing due to unintended accesses.
— Input capture
A read from an input capture channel register causes the corresponding channel flag, CxF, to
be cleared in the TFLG1 register.
— Output compare
A write to the output compare channel register causes the corresponding channel flag, CxF, to
be cleared in the TFLG1 register.
— Timer counter
Any access to the TCNT register clears the TOF flag in the TFLG2 register.
— Pulse accumulator A
Any access to the PACN3 and PACN2 registers clears the PAOVF and PAIF flags in the
PAFLG register.
— Pulse accumulator B
Any access to the PACN1 and PACN0 registers clears the PBOVF flag in the PBFLG register.
— Modulus down counter
Any access to the MCCNT register clears the MCZF flag in the MCFLG register.
11.4.2 Reset
The reset state of each individual bit is listed within the register description section (Section 11.3,
“Memory Map and Register Definition”) which details the registers and their bit-fields.