Chapter 3 4 Kbyte EEPROM Module (S12XEETX4KV2)
MC9S12XDP512 Data Sheet, Rev. 2.11
Freescale Semiconductor 159
3.4.1.2 Command Write Sequence
The EEPROM command controller is used to supervise the command write sequence to execute program,
erase, erase verify, sector erase abort, and sector modify algorithms.
Before starting a command write sequence, the ACCERR and PVIOL flags in the ESTAT register must be
clear (see Section 3.3.2.6, “EEPROM Status Register (ESTAT)”) and the CBEIF flag should be tested to
determine the state of the address, data and command buffers. If the CBEIF flag is set, indicating the
buffers are empty, a new command write sequence can be started. If the CBEIF flag is clear, indicating the
buffers are not available, a new command write sequence will overwrite the contents of the address, data
and command buffers.
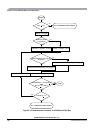
A command write sequence consists of three steps which must be strictly adhered to with writes to the
EEPROM module not permitted between the steps. However, EEPROM register and array reads are
allowed during a command write sequence. The basic command write sequence is as follows:
1. Write to one address in the EEPROM memory.
2. Write a valid command to the ECMD register.
3. Clear the CBEIF flag in the ESTAT register by writing a 1 to CBEIF to launch the command.
The address written in step 1 will be stored in the EADDR registers and the data will be stored in the
EDATA registers. If the CBEIF flag in the ESTAT register is clear when the first EEPROM array write
occurs, the contents of the address and data buffers will be overwritten and the CBEIF flag will be set.
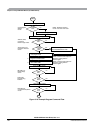
When the CBEIF flag is cleared, the CCIF flag is cleared on the same bus cycle by the EEPROM command
controller indicating that the command was successfully launched. For all command write sequences
except sector erase abort, the CBEIF flag will set four bus cycles after the CCIF flag is cleared indicating
that the address, data, and command buffers are ready for a new command write sequence to begin. For
sector erase abort operations, the CBEIF flag will remain clear until the operation completes. Except for
the sector erase abort command, a buffered command will wait for the active operation to be completed
before being launched. The sector erase abort command is launched when the CBEIF flag is cleared as part
of a sector erase abort command write sequence. Once a command is launched, the completion of the
command operation is indicated by the setting of the CCIF flag in the ESTAT register. The CCIF flag will
set upon completion of all active and buffered commands.
3.4.2 EEPROM Commands
Table 3-10 summarizes the valid EEPROM commands along with the effects of the commands on the
EEPROM block.
Table 3-10. EEPROM Command Description
ECMDB Command Function on EEPROM Memory
0x05 Erase
Verify
Verify all memory bytes in the EEPROM block are erased. If the EEPROM block is erased, the
BLANK flag in the ESTAT register will set upon command completion.
0x20 Program Program a word (two bytes) in the EEPROM block.
0x40 Sector
Erase
Erase all four memory bytes in a sector of the EEPROM block.