512 Kbyte Flash Module (S12XFTX512K4V2)
BookTitle, Rev. 2.4
112 Freescale Semiconductor
2.3.2.5 Flash Protection Register (FPROT)
The FPROT register defines which Flash sectors are protected against program or erase operations.
All bits in the FPROT register are readable and writable with restrictions (see Section 2.3.2.5.1, “Flash
Protection Restrictions”) except for RNV[6] which is only readable.
During the reset sequence, the FPROT register is loaded from the Flash Configuration Field at global
address 0x7F_FF0D. To change the Flash protection that will be loaded during the reset sequence, the
upper sector of the Flash memory must be unprotected, then the Flash Protect/Security byte located as
described in Table 2-1 must be reprogrammed.
Trying to alter data in any protected area in the Flash memory will result in a protection violation error and
the PVIOL flag will be set in the FSTAT register. The mass erase of a Flash block is not possible if any of
the Flash sectors contained in the Flash block are protected.
Table 2-10. Flash Register Bank Selects
BKSEL[1:0] Selected Block
00 Flash Block 0
01 Flash Block 1
10 Flash Block 2
11 Flash Block 3
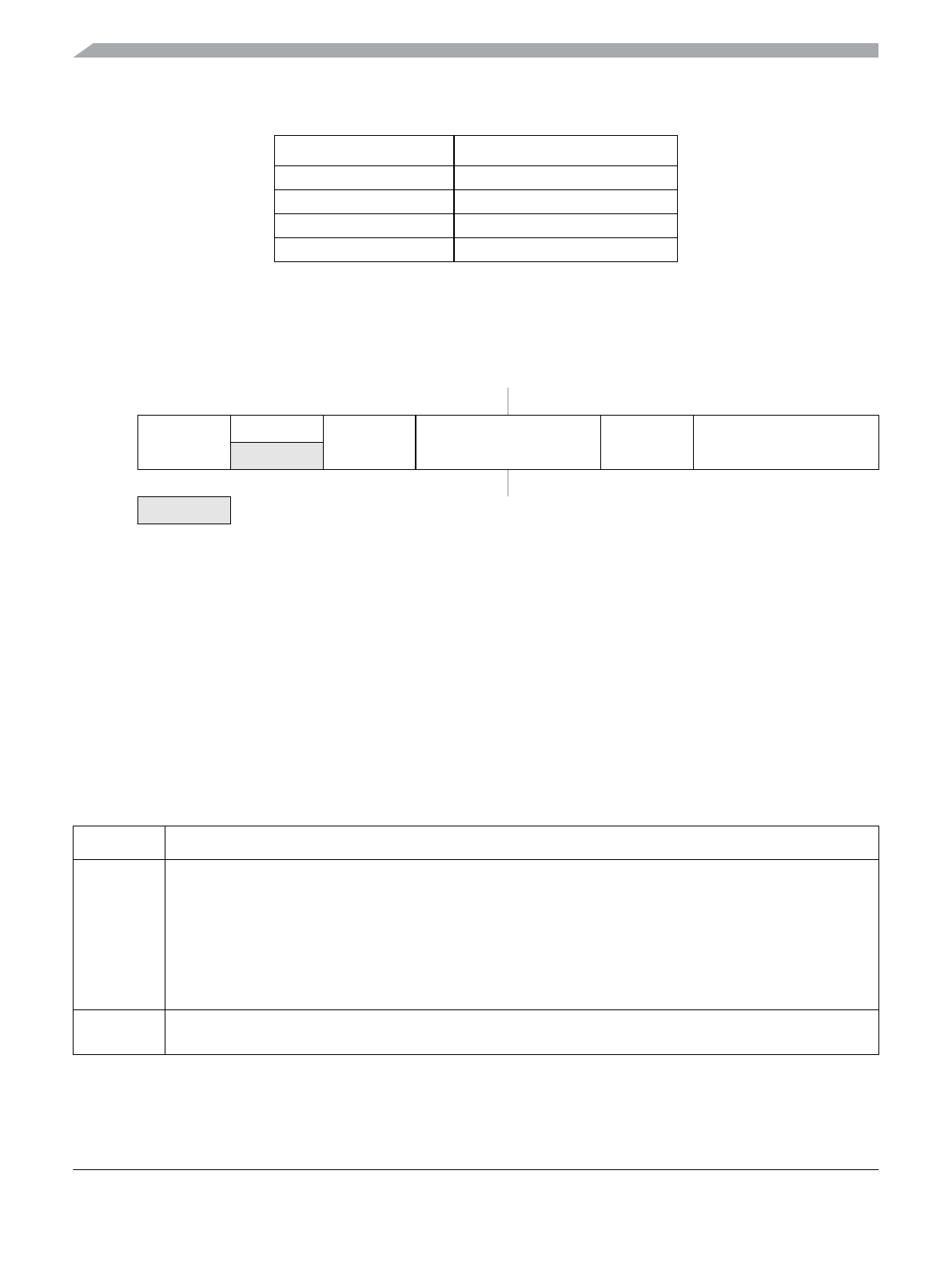
Module Base + 0x0004
76543210
R
FPOPEN
RNV6
FPHDIS FPHS FPLDIS FPLS
W
Reset F F F FFFFF
= Unimplemented or Reserved
Figure 2-10. Flash Protection Register (FPROT)
Table 2-11. FPROT Field Descriptions
Field Description
7
FPOPEN
Flash Protection Open — The FPOPEN bit determines the protection function for program or erase as shown
in Table 2-12.
0 The FPHDIS and FPLDIS bits define unprotected address ranges as specified by the corresponding
FPHS[1:0] and FPLS[1:0] bits. For an MCU without an EEPROM module, the FPOPEN clear state allows the
main partof the Flash block to be protected while a small address range can remain unprotected for EEPROM
emulation.
1 The FPHDIS and FPLDIS bits enable protection for the address range specified by the corresponding
FPHS[1:0] and FPLS[1:0] bits.
6
RNV6
Reserved Nonvolatile Bit — The RNV[6] bit should remain in the erased state for future enhancements.


















