6 - 18
6. APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
6.9 Software limit
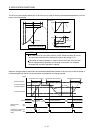
(1) Using a JOG operation
During JOG operation, if the software limit is reached, a reached software limit (operation alarm A2, detail
01) occurs, the deceleration of the servo is started, and the servo is stopped not to exceed the software
limit.
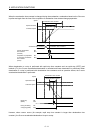
(2) Using incremental feed
If the movement amount designated by an incremental feed exceeds the software limit, an out of software
limit boundaries (operation alarm A1, detail 01) occurs and the start operation is not performed.
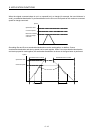
(3) Using automatic operation
If the point designated by a position command exceeds the software limit, an out of software limit
boundaries (operation alarm A1, detail 01) occurs and the start operation is not performed. Also, if the point
is designated during operation, an out of software limit boundaries (operation alarm A1, detail 01) occurs
when the point is designated and servo is decelerated and stopped.
(4) Using linear interpolation
If the point designated by a position command for an axis within the group exceeds the software limit, an
out of software limit boundaries (operation alarm A1, detail 01) occurs and the start operation is not
performed. Also, if the point is designated during operation, an alarm occurs when the point is designated
and servo is decelerated and stopped.
POINT
If the deceleration check method is in continuous operation and the position
command after point switching exceeds the software limit, it will output the out
of software limit boundaries (operation alarm A1, detail 01) and will come to a
decelerated stop. In this case, if the distance to the software limit is shorter
than the distance necessary to make a decelerated stop, it may stop outside
the software limit.
The software limit boundaries are set using parameters No. 0228, 0229,
022A, 022B.
If an alarm set due to exceeding the software limit, the servo is stopped using
the deceleration time constant.
API LIBRARY
Use the sscChange2Parameter/sscCheck2Parameter function to set/get the
software limit.