6 - 6
6. APPLICATION FUNCTIONS
6.2.2 Setting example of speed units
The following is a setup example for use of mm/min as a speed unit for a piece of equipment that uses ball
screws.
(1) Equipment specification
The equipment specification is same as that of Section 6.1.
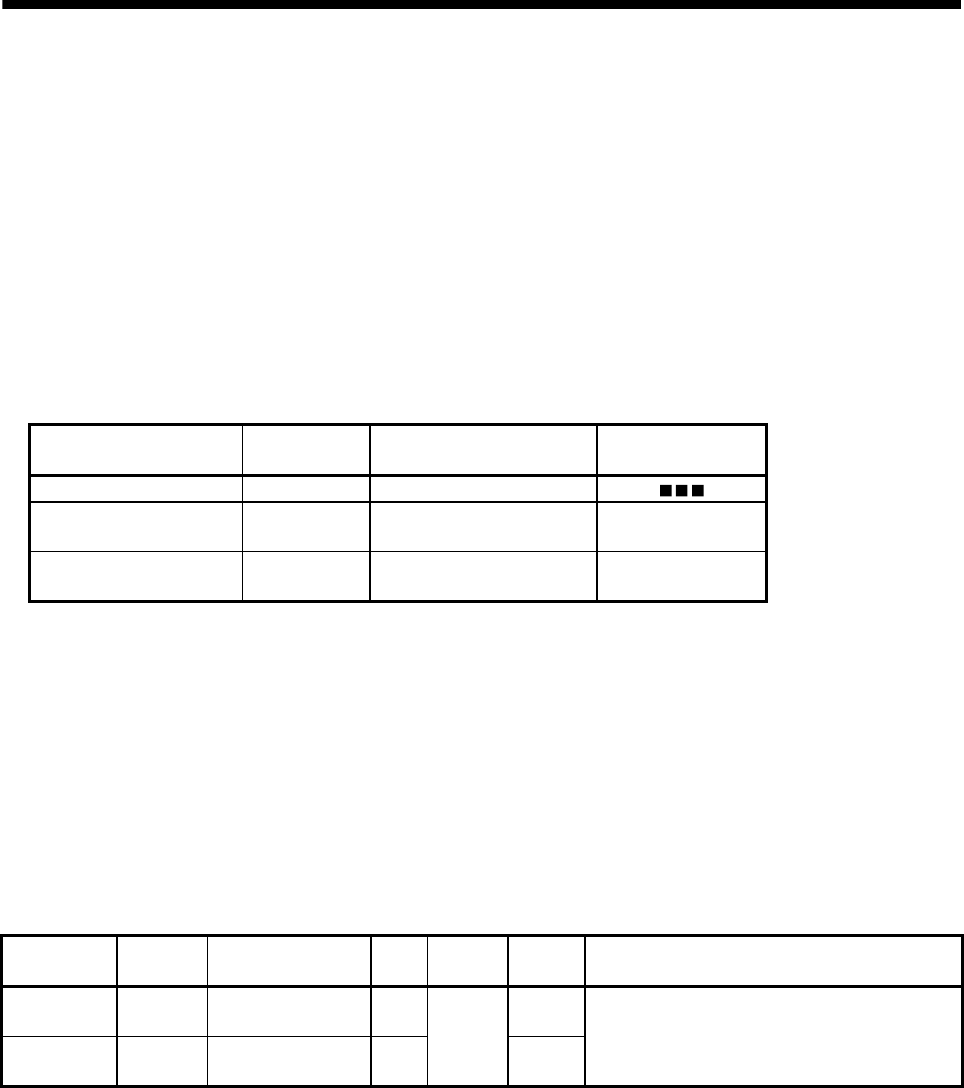
(2) Parameter setting for the speed unit
As the position command unit is µm, set 1000 to the speed units multiplication factor to use mm/min as a
speed unit.
1000µm/min = 1mm/min
Parameter No.
(Note)
Abbreviation
Name Setting value
0200 *OPC1 Control option 1 0 h
020E SUML Speed units multiplication
factor (lower)
03E8h
020F SUMH Speed units multiplication
factor (upper)
0000h
Note. The settings for the parameters with a * mark at the front of the abbreviation are validated when
the system is restarted.
6.2.3 Speed limit
The following restrictions apply to the command speed. Reexamine the command speed according to the
following.
(1) When the speed command exceeds the speed limit (parameter No.0222, 0223), the speed is limited to the
speed limit.
Control parameters
Parameter No.
bbreviation Name
Initial
Value
Unit
Setting
range
Function
0222 SPLL Speed limit value
(lower)
0BB8h Speed
units
0000h to
FFFFh
Set the value for the moving speed limit.
0223 SPLH Speed limit value
(upper)
0000h 0000h to
7FFFh
(2) When the command speed output to the servo amplifier exceeds the motor maximum revolution speed, the
speed is limited to the motor maximum revolution speed. The motor maximum revolution speed can be
checked in the motor maximum revolution speed (monitor No.0114) and the motor permissible pulse rate
(monitor No.0120, 0121).
(3) The position board calculates the command speed of the servo amplifiers using the speed setting, speed
units multiplication factor and electronic gears; however, if an overflow occurs in the calculation process
due to high command speed etc., the speed is limited to the calculable maximum value. The calculable
maximum value is checked in the maximum output pulse rate (monitor No.0122, 0123) of the servo
information.
