8291
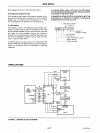
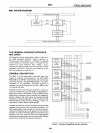
PIN DESCRIPTION
Symbol
Do-D7
RSo-RS2
DREQ
I/O
Pin
No. Function
I/O
12-19 Data bus port, to be connected
to microprocessor data bus.
o
o
21-23 Register select inputs, to be
con-
nected
to
three
non-multiplexed
microprocessor
address bus
lines. Select which of the 8
in-
ternal read (write) registers will
be read from (written into) with
the execution of RD (WR).
8
9
10
11
6
Chip
select. When low, enables
reading from
or
writing
into
the
register selected by
RSo-RS2.
Read strobe. When low, selected
register contents are read
by
the
CPU.
Write strobe. When low, data is
written
into
the selected register.
Interrupt
request to the
micro-
processor, set high for request
and cleared when the
appropri-
ate register is accessed
by
the
CPU. May be software
config-
ured
to
be active low.
DMA
request,
normally
low, set
high
to
indicate byte
output
or
byte input, in
DMA
mode; reset
by
DACK.
DACK
7
DMA
acknowledge. When low,
resets DREQ and selects data
in/data
out
register
for
DMA
data transfer (actual transfer
done
by
RD/WR pulse).
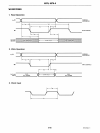
TRIG 0
5
CLOCK
3
RESET 4
I/O
36
Must
be high if
DMA
is
not
used.
Trigger
output,
normally
low;
generates a
triggering
pulse with
1!,sec min. width in response
to
the GET bus command
or
Trigger
auxiliary command.
External
clock
input, used
only
for
T 1 delay generator. May be
any
speed in 1-8 MHz range.
Reset input. When high, forces
the device
into
an
"Idle"
(initiali-
zation) mode. The device will re-
main at
"Idle"
until released
by
the microprocessor.
8-bit
GPIB data port, used
for
bidirectional
data byte transfer
between
8291
and GPIB via
non-
inverting
external line trans-
ceivers.
Data valid; GPIB handshake
control
line. Indicates the avail-
ability
and validity
of
infor-
mation
on the DIO lines.
9-83
Symbol
NRFD
T/R1
T/R2
Vee
GND
I/O
Pin
No. Function
I/O
37
Not ready
for
data; GPIB
hand-
shake
control
line. Indicates the
condition
of
readiness
of
de-
vicels)
connected
to
the bus to
accept data.
I/O
38
Not data accepted; GPIB
hand-
shake
control
line. Indicates the
condition
of
acceptance
of
data
by the device(s) connected
to
the bus.
26
24
o
27
25
I/O
39
o
o 2
P.S.
40
P.S.
20
Attention; GPIB
command
line.
Specifies
how
data on DIO lines
are to be interpreted.
Interface clear; GPIB
command
line. Places the interface
func-
tions in a
known
quiescent state.
Service request;
GPIB
command
line. Indicates the need
for
attention and requests
an
inter-
ruption
of
the
current
sequence
of events on the
GPIB.
Remote enable;
GPIB
command
line. Selects (in
conjunction
with
other messages I remote
or
local
control
of the device.
End
or
identify; GPIB
command
line. Indicates the end of a
multiple
byte transfer sequence
or,
in
conjunction
with
ATN,
addresses the device
during
a
polling sequence.
External transceivers
control
line. Set
high
to
indicate
output
data/signals
on
the D101-D108
and DAV lines and
input
signals
on
the NRFD and
NDAC
lines
(active source handshake
I.
Set
low
to
indicate
input
data/
signals on the D101·D108 and
DAV
lines and
output
signals on
the NRFD and
NDAC
lines (ac-
tive
acceptor
handshake I.
External transceivers
control
line. Set
high
to
indicate
output
signals on the EOI line. Set
low
to
indicate
expected
input
signal
on the EOI line
during
parallel
poll.
Positive
power
supply
(5V ±
10%).
Potential
ground
circuit.
Note:
All
signals
on
the
8291
pins are specified with positive logic.
However,
IEEE 488 specifies negative
l~
on
its
16 signal lines. Thus, the
data
is
inverted once from
00-07
to
0101-0108
and non-inverting bus
transceivers should
be
used.