8255A18255A·5
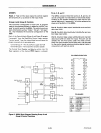
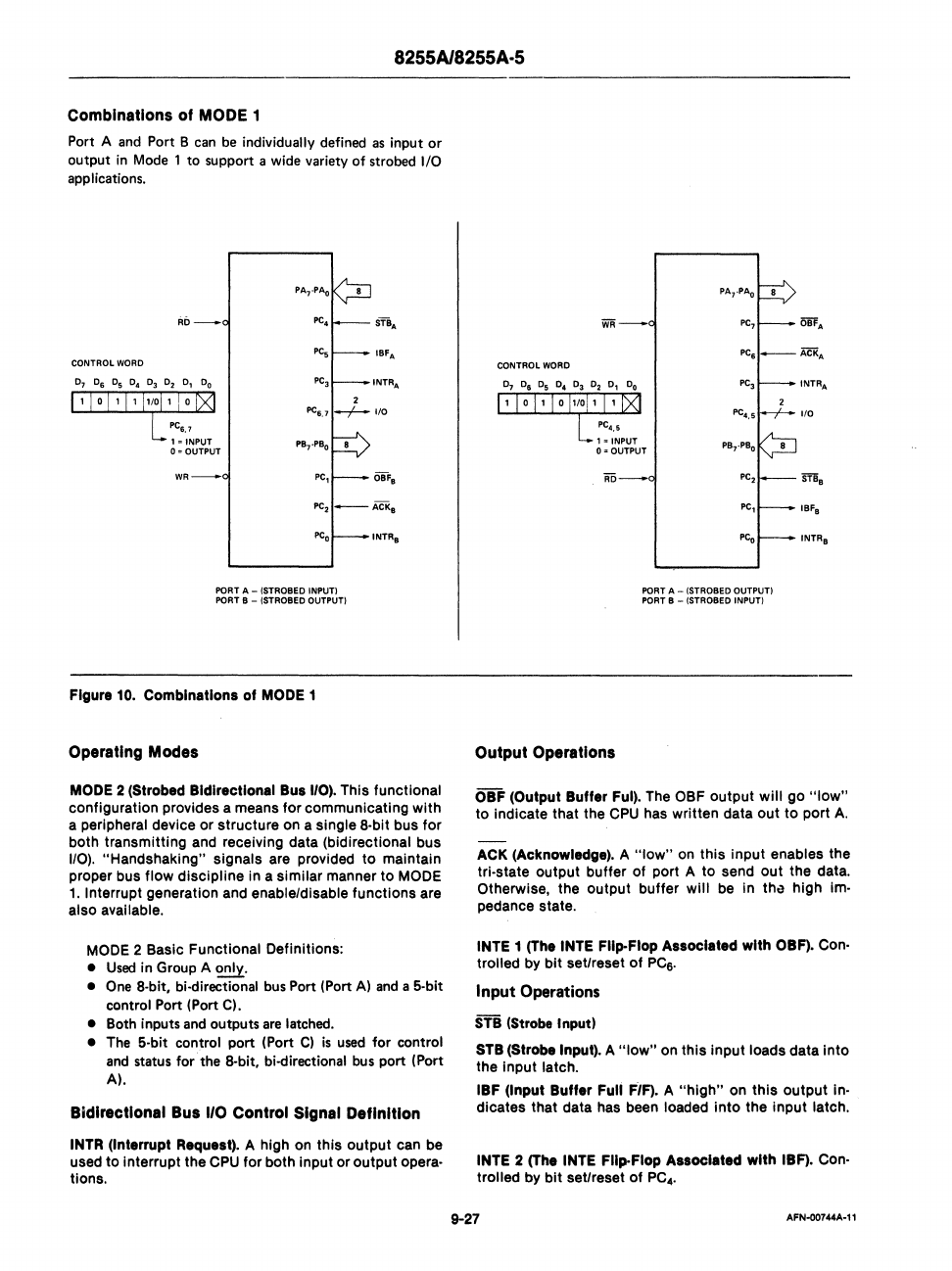
Combinations of MODE 1
Port A
and
Port B
can
be
individually defined
as
input
or
output
in
Mode 1 to support a wide variety of strobed I/O
applications.
PA
7
,PAn
PC,
STB
A
PC,
IBFA
PC,
INTRA
2
Pe
6
.
7
-+-- I/O
pe
"
PD
O
8
PC,
pe
2
-ACK
B
PORT A - (STROBED INPUT)
PORT
B - (STROBED OUTPUT)
Figure
10.
Combinations
01
MODE 1
Operating Modes
INTRB
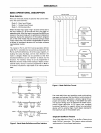
MODE 2 (Strobed Bidirectional Bus
1/0).
This functional
configuration provides a means
for
communicating
with
a peripheral device
or
structure on a single S·bit bus
for
both transmitting and receiving data (bidirectional bus
1/0).
"Handshaking" signals are provided
to
maintain
proper bus
flow
discipline
in a similar manner to MODE
1.
Interrupt generation and enableldisable functions are
also available.
MODE 2 Basic Functional Definitions:
•
Used
in Group A only.
•
One
S-bit, bi-directional
bus
Port (Port A)
and
a 5-bit
control Port (Port
C).
•
Both inputs
and
outputs
are
latched.
• The 5-bit control port (Port
C)
is
used
for
control
and
status
for
the B-bit, bi-directional
bus
port (Port
A).
Bidirectional Bus 1/0 Control Signal Definition
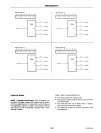
INTR (Interrupt Request). A high on
this
output
can be
used
to
Interrupt the
CPU
for
both input or output opera-
tions.
Output Operations
PC,
PC.
PORT
A - (STROBED OUTPUT)
PORT B - (STROBED INPUT)
I/O
INTRa
OBF (Output Buffer Ful). The OBF
output
will
go
"low"
to
indicate that the
CPU
has written data
out
to
port
A.
ACK (Acknowledge). A
"low"
on this input enables the
tri-state output buffer of port A to send
out
the data.
Otherwise, the output buffer
will
be In the high im-
pedance state.
INTE 1 (The INTE Flip-Flop Associated
with
OBF)_
Con-
trolled
by
bit
setlreset
of
PCs.
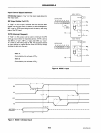
Input
Operations
STB
(Strobe Input)
STB (Strobe Input)_ A
"low"
on
this
input
loads data
into
the Input latch.
IBF (Input Buffer Full
F/F)_
A
"high"
on
this
output
in-
dicates that data has been loaded
into
the
input
latch.
INTE 2 (The INTE Flip-Flop Associated
with
IBF)_
Con-
trolled
by
bit
setlreset of
PC
4
•
9-27
AFN-00744A-11