THE SINGLE COMPONENT MCS-48™ SYSTEM
2.0 Summary
Sections
2.1
through 2.4 describe in detail
the functional characteristics
of
the 8748
EPROM, 8048/8049 ROM and 8035/8039
single component microcomputers. Unless
otherwise noted, details within these sec-
tions apply to
all .versions. Sections
2.5
through
2.11
describe the operation of the
8021, while Sections 2.12 through
2.21
de-
scribe the
8022. This chapter is limited to
those functions useful in single-chip imple-
mentations
of
the MCS-48. Chapter 3 dis-
cusses functions which allow expansion of
program memory, data memory, and input-
output
capability.
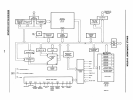
2.1
Architecture
The following sections break the 8048 into
functional blocks and describe each
in
detail.
2.1.1
Arithmetic Section
The arithmetic section of the processor con-
tains the basic data manipulation functions of
the 8048
and
can be divided into the following
blocks:
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Accumulator
Carry Flag
Instruction Decoder
In a typical operation data stored in the
accumulator
is
combined
in
the
ALU
with data
from another source
on
the internal bus (such
as a register or
I/O port) and the result is
stored
in
the accumulator or another register.
The following is a more detailed description of
the function of each block:
Instruction
Decoder
The operation code (op code) portion of each
program instruction is stored
in
the Instruction
Decoder and converted to outputs which
control the function of each of the blocks of
the Arithmetic Section. These lines control
the source of data and the destination register
as
well
as
the function performed
in
the
ALU.
2-1
Arithmetic Logic Unit
The
ALU
accepts 8-bit data words from one
or
two
sources and generates
an
8-bit result
under control
of
the Instruction Decoder.
The
ALU
can
perform
the
following functions:
Add With
or
Without Carry
AND,
OR, Exclusive
OR
I ncrementiDecrement
Bit Complement
Rotate Left, Right
Swap Nibbles
BCD Decimal Adjust
If the operation performed by the ALU results
in
a value represented
by
more than 8 bits
(overflow of most significant bit) a Carry Flag
is set
in
the Program Status Word.
Accumulator
The accumulator is the single most impor-
tant data register in the processor, being
one of the sources
of
input to the ALU and
often the destination
of
the result
of
opera-
tions performed in the ALU. Data to and
from
1/0 ports and memory also normally
passes through the accumulator.
2.1.2
Program Memory
Resident program memory consists
of
1024
or
2048 words eight bits wide which are
addressed by the program counter.
In the
8748 this memory is user programmable
and erasable
EPROM; in the 8048/8049 the
memory is ROM which is mask program-
mable at the factory. The
8035/8039
has no
internal program memory and is used with
external devices. Program code is com-
pletely interchangeable among the various
versions. See Section
2.3
for
EPROM pro-
gramming techniques.