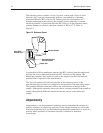
Operating Principles IĆ11
The pCO
2
sensor is based upon the electrode described by Severinghaus and
Bradley.
15
It is a complete electrochemical cell that consists of a measuring
electrode and an internal reference electrode. The measuring electrode, which is a
pH electrode, is surrounded by a chloride bicarbonate solution. A membrane
permeable to gaseous CO
2
separates this solution from the sample. The internal
reference electrode, which contains a silver/silver chloride electrode surrounded by
the chloride-bicarbonate solution, provides a fixed potential.
Sample Path
Measuring Electrode
Contact
Internal Reference
Electrode Contact
As the sample comes in contact with the membrane, CO
2
diffuses into
the chloride-bicarbonate solution, which causes a change in the hydrogen ion
activity.
CO
2
+ H
2
O { HCO
3
–
+ H
+
The internal pH electrode detects the change in hydrogen concentration occurring
in the chloride bicarbonate solution and generates a half-cell potential. This
potential, when compared to the fixed potential of the reference electrode, results
in a measurement that reflects pH change in the chloride bicarbonate solution. The
change in pH is related to the log of the partial pressure of CO
2
.
Oxygen (O
2
) is essential for cell and tissue metabolism in the body. The
cardiopulmonary system is responsible for transporting oxygen to the cells.
Oxygen transport involves four major steps: convection and diffusion from the air
into the pulmonary circulation, combination of O
2
from the lungs with hemoglobin
in red blood cells, transportation of the O
2
through the arteries to the cell, and
finally the release into the tissues and utilization of O
2
at the cellular level.