Functions and Examples
Issue 4 September 1995
10-9
Now, let’s take a look at the following table, which illustrates the skill preferences
assigned for one specific VDN (3333) that is used for the auto club:
In this table, note that the first VDN skill Preference corresponds to a knowledge
area that could be considered a ‘‘subset’’ of the knowledge area represented by
the second (and, taking it a step further, the third) Preference. Similarly, the
second VDN skill Preference corresponds to a knowledge area that could be
considered a "subset" of the knowledge area represented by the third
Preference. Such an approach is commonly used to assign VDN skill
preferences. The result of this approach is that the longer a call waits, the larger
the pool of agents that the ACD considers for handling the call.
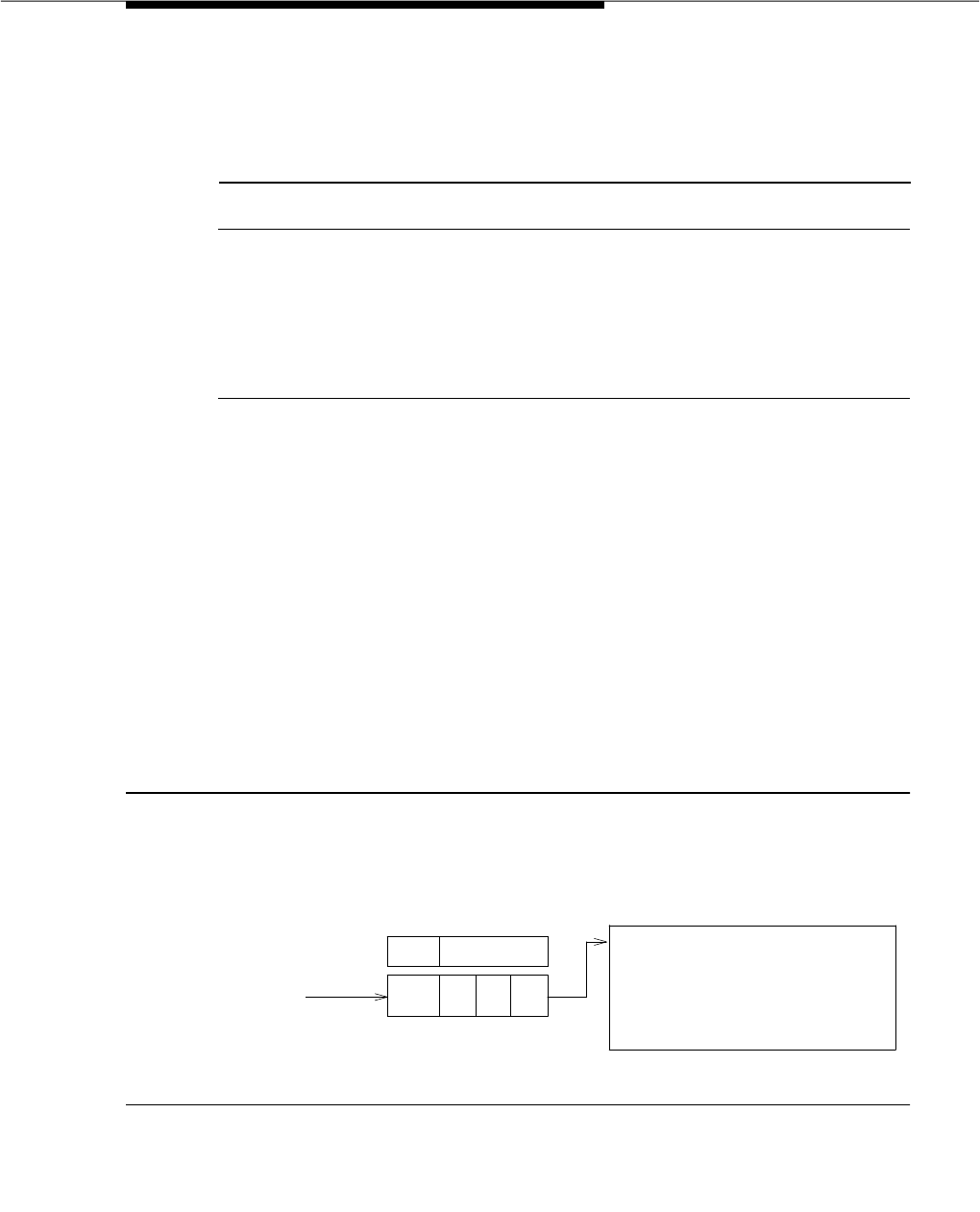
Now, recall that the vector number to which each VDN associated with the auto
club has already been provided in Table 10-5 of this section. A quick glance at
the table shows that VDN 3333 points to Vector 3. As such, the skill requirements
associated with the VDN are ‘‘passed along’’ to the vector. This process can
be illustrated as follows:
Figure 10-2. Example of VDN Skill Implementation
Let’s assume that the English-speaking caller needs information on Route
Planning and dials the appropriate number (555-3333). In such a case, the call
Table 10-6. Skill Preferences Assignments for VDN 3333
VDN 3333 - Skill Preferences
1st: 33 Directed to an agent who is knowledgeable about
Route Planning and speaks English
2nd: 44 Directed to an agent who is knowledgeable about
Route Planning and is bilingual
3rd: 99 Directed to an agent who can field all calls
VECTOR 3
443333 33 99
Route Planning (English)
555-3333
PUBLISHED
NUMBER
VECTOR DIRECTORY
SKILLS NO.
1. queue-to main skill 1st pri h
2. announcement 1234
3. queue-to main skill 2nd pri h
4. wait-time 10 secs hearing music
5. queue-to main skill 3rd pri h


















