8XC196NP, 80C196NU USER’S MANUAL
13-42
13.9.2 Explanation of AC Symbols
Each symbol consists of two pairs of letters prefixed by “T” (for time). The characters in a pair
indicate a signal and its condition, respectively. Symbols represent the time between the two sig-
nal/condition points. For example,
T
LLRL
is the time between signal L (ALE) condition L (Low)
and signal R (RD#) condition L (Low). Table 13-15 defines the signal and condition codes.
13.9.3 AC Timing Definitions
Table 13-16 defines the AC timing specifications that the memory system must meet and those
that the device will provide.
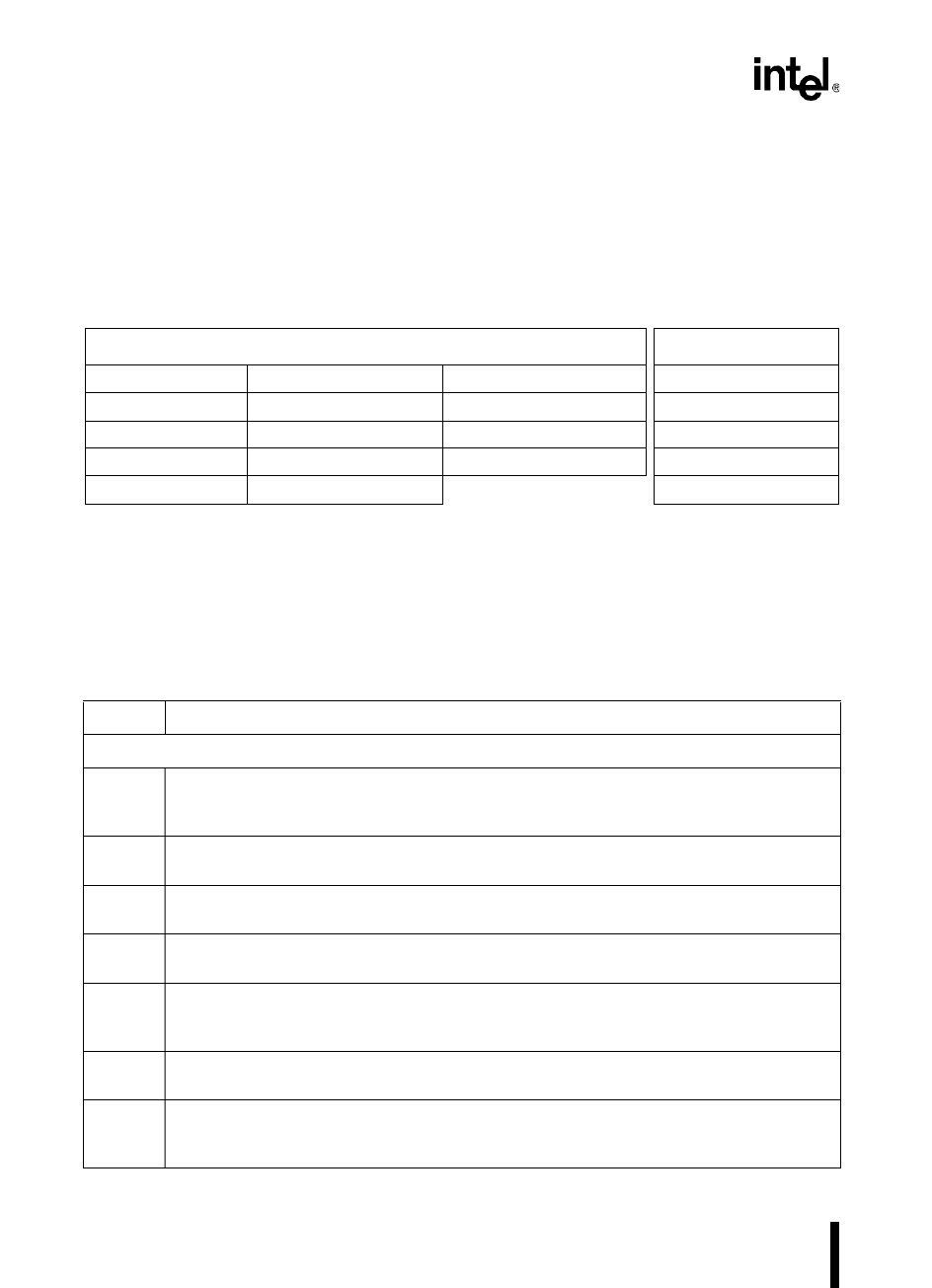
Table 13-15. AC Timing Symbol Definitions
Signals Conditions
A
†
Address H HOLD# S CS
x
# H High
B BHE# HA HLDA# W WR#, WRH#, WRL# L Low
C CLKOUT L ALE X XTAL1 V Valid
D Data Q Data Out Y READY X No Longer Valid
G Buswidth R RD# Z Floating
†
Address bus (demultiplexed mode) or address/data bus (multiplexed mode)
Table 13-16. AC Timing Definitions
Symbol Definition
The External Memory System Must Meet These Specifications
T
AVDV
Address Valid to Input Data Valid
Maximum time the memory device has to output valid data after the device outputs a valid
address.
T
CHDV
CLKOUT High to Input Data Valid
Maximum time the memory system has to output valid data after CLKOUT rises.
T
CLDV
CLKOUT Low to Input Data Valid
Maximum time the memory system has to output valid data after CLKOUT falls.
T
QVWH
Data Valid to WR# High
Time between data being valid on the bus and WR# going inactive.
T
RHDZ
RD# High to Input Data Float
Time after RD# is inactive until the memory system must float the bus. If this timing is not met,
bus contention will occur.
T
RLDV
RD# Low to Input Data Valid
Maximum time the memory system has to output valid data after the device asserts RD#.
T
SLDV
CS
x
# Valid to Input Data Valid
Maximum time the memory device has to output valid data after the device outputs a valid chip-
select output.


















