12-3
SPECIAL OPERATING MODES
12.2 REDUCING POWER CONSUMPTION
Each power-saving mode conserves power by disabling portions of the internal clock circuitry
(Figure 12-1 and Figure 12-2). The following paragraphs describe each mode in detail.
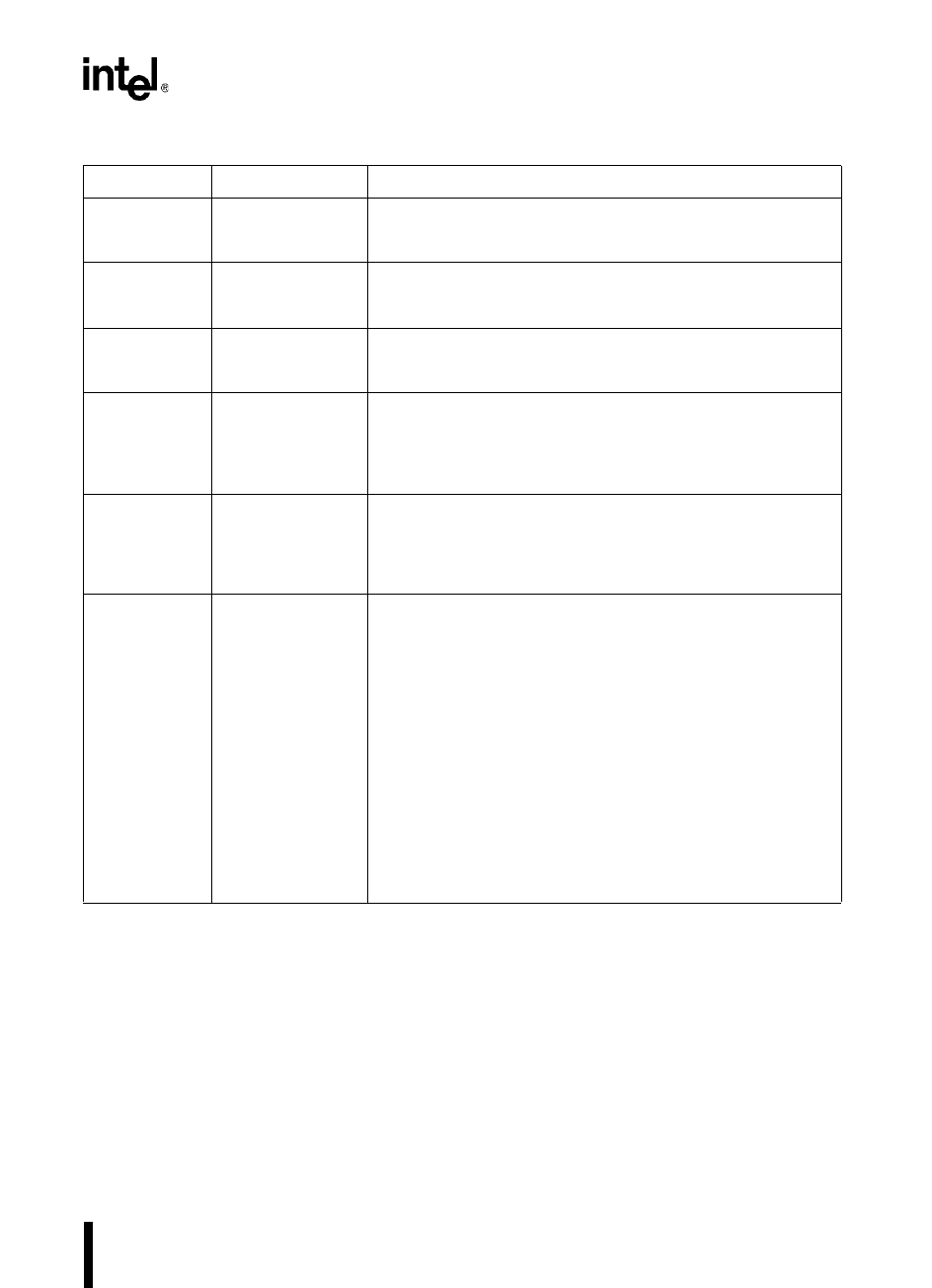
INT_MASK1 0013H Interrupt Mask 1
Bits 5 and 6 of this register enable and disable (mask) the
external interrupts, EXTINT2 and EXTINT3.
INT_PEND 0009H Interrupt Pending
Bits 3 and 4 of this register are set to indicate a pending external
interrupt, EXTINT0 and EXTINT1.
INT_PEND1 0012H Interrupt Pending 1
Bits 5 and 6 of this register are set to indicate a pending external
interrupt, EXTINT2 and EXTINT3.
P2_DIR
P3_DIR
1FD3H
1FDAH
Port
x
Direction
Each bit of P
x
_DIR controls the direction of the corresponding pin.
Clearing a bit configures a pin as a complementary output; setting
a bit configures a pin as an input or open-drain output. (Open-
drain outputs require external pull-ups.)
P2_MODE
P3_MODE
1FD1H
1FD8H
Port
x
Mode
Each bit of P
x
_MODE controls whether the corresponding pin
functions as a standard I/O port pin or as a special-function
signal. Setting a bit configures a pin as a special-function signal;
clearing a bit configures a pin as a standard I/O port pin.
P2_REG
P3_REG
1FD5H
1FDCH
Port
x
Data Output
For an input, set the corresponding P
x
_REG bit.
For an output, write the data to be driven out by each pin to the
corresponding bit of P
x
_REG. When a pin is configured as
standard I/O (P
x
_MODE.
y
= 0), the result of a CPU write to
P
x
_REG is immediately visible on the pin. When a pin is
configured as a special-function signal (P
x
_MODE.
y
= 1), the
associated on-chip peripheral or off-chip component controls the
pin. The CPU can still write to P
x
_REG, but the pin is unaffected
until it is switched back to its standard I/O function.
This feature allows software to configure a pin as standard I/O
(clear P
x
_MODE.
y
), initialize or overwrite the pin value, then
configure the pin as a special-function signal (set P
x
_MODE.
y
). In
this way, initialization, fault recovery, exception handling, etc., can
be done without changing the operation of the associated
peripheral.
Table 12-2. Operating Mode Control and Status Registers (Continued)
Mnemonic Address Description


















