5-27
MEMORY PARTITIONS
Data accesses to 002000–002FFFH depend on the REMAP bit and the EA# input:
• If remapping is disabled (CCB1.2 = 0), accesses are external.
• If remapping is enabled (CCB1.2 = 1), accesses depend on EA#:
— If EA# is low, accesses are external (REMAP is ignored).
— If EA# is high, accesses are to the internal ROM.
5.6 MEMORY CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES
This section provides examples of memory configurations for both 64-Kbyte and 1-Mbyte mode.
Each example consists of a circuit diagram and a memory map that describes how the address
space is implemented. Chapter 13, “Interfacing with External Memory,” discusses the interface
in detail and provides additional examples.
5.6.1 Example 1: Using the 64-Kbyte Mode
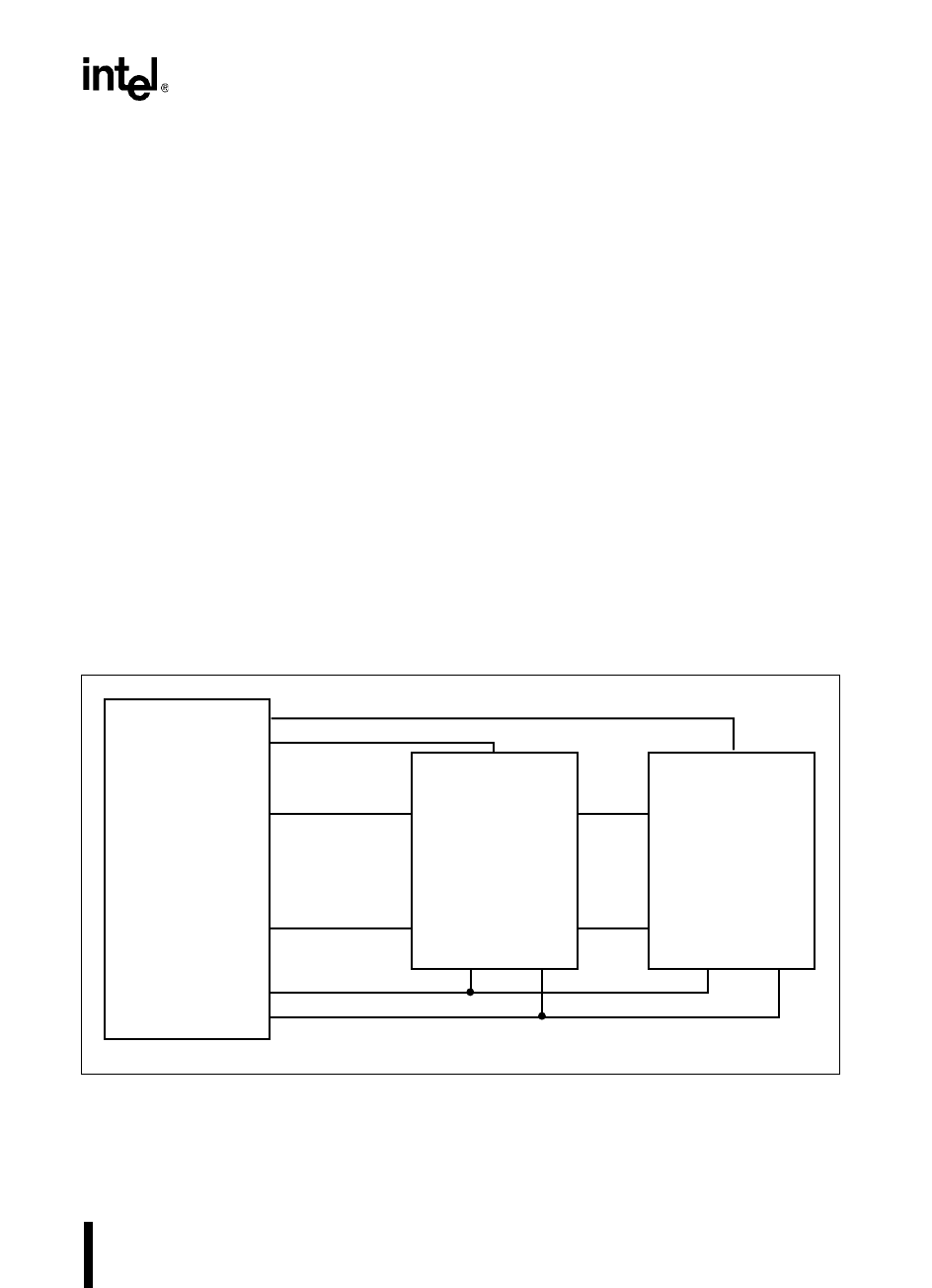
Figure 5-9 shows a system designed for operation in the 64-Kbyte mode. Code executes only
from page FFH, which is implemented by the 64-Kbyte flash memory. The 32-Kbyte RAM in the
upper half of page 00H stores near data. Table 5-12 on page 5-28 lists the memory addresses for
this example. (For memory map details, see Table 5-1 on page 5-4.)
Figure 5-9. A 64-Kbyte System With an 8-bit Bus
80C196NP and 80C196NU: The flash memory, which implements page FFH, holds the special-
purpose memory (FF2000–FF207FH), code, and far constants.
A2474-02
Flash
64Kx8
Code & Data
FF0000–
FFFFFFH
CE#
Page FFH
A15:0
D7:0
OE# WE#
RAM
32Kx8
Data
008000–
00FFFFH
CE#
Page 00H
A14:0
D7:0
OE# WE#
8XC196NP, NU
A15:0
AD7:0
RD#
WR#
CS1#
CS0#
A14:0
AD7:0
A15:0
AD7:0


















