8-13
SERIAL I/O (SIO) PORT
8.4.4 Enabling the Serial Port Interrupts
The serial port has both a transmit interrupt (TI) and a receive interrupt (RI). To enable an inter-
rupt, set the corresponding mask bit in the interrupt mask register (see Table 8-2 on page 8-2) and
execute the EI instruction to globally enable servicing of interrupts. See Chapter 6, “Standard and
PTS Interrupts,” for more information about interrupts.
8.4.5 Determining Serial Port Status
You can read the SP_STATUS register (Figure 8-8) to determine the status of the serial port.
Reading SP_STATUS clears all bits except TXE. For this reason, we recommend that you copy
the contents of the SP_STATUS register into a shadow register and then execute bit-test instruc-
tions such as JBC and JBS on the shadow register. Otherwise, executing a bit-test instruction
clears the flags, so any subsequent bit-test instructions will return false values. You can also read
the interrupt pending register (see Table 8-2 on page 8-2) to determine the status of the serial port
interrupts.
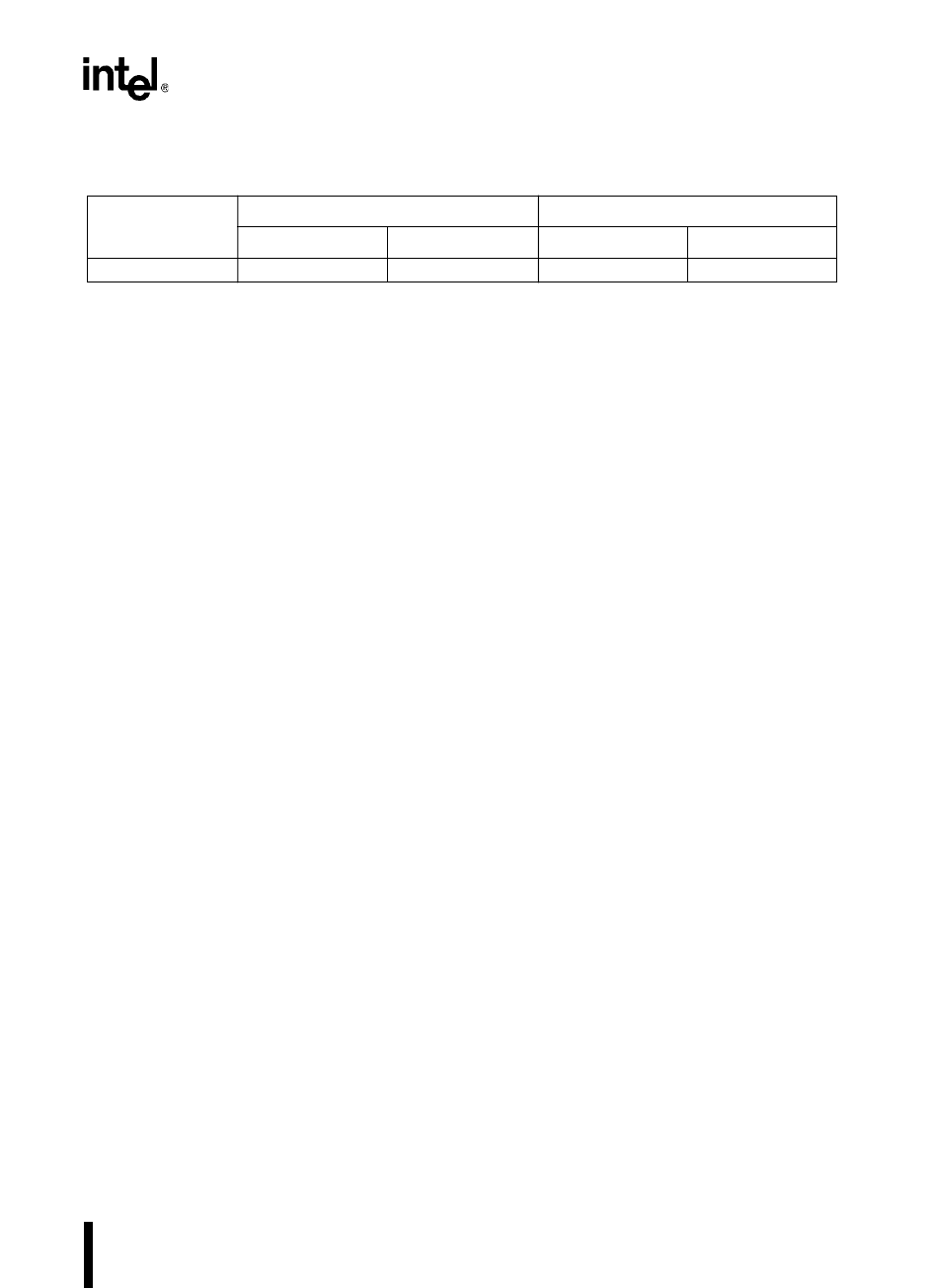
Table 8-4. SP_BAUD Values When Using the Internal Clock at 50 MHz (80C196NU Only)
Baud Rate
SP_BAUD Register Value
†
% Error
Mode 0 Mode 1, 2, 3 Mode 0 Mode 1, 2, 3
9600 8A2CH 8145H 0 0.15
†
Bit 15 is always set when the internal peripheral clock is selected as the clock source for the baud-rate
generator.


















