System Security
Polycom, Inc. 40
How Certificates Are Used by the Polycom RealPresence DMA System
The Polycom RealPresence DMA system uses X.509 certificates in the following ways:
1 When a user logs into the Polycom RealPresence DMA system’s browser-based management
interface, the Polycom RealPresence DMA system (server) offers an X.509 certificate to identify
itself to the browser (client).
The Polycom RealPresence DMA system’s certificate must have been signed by a certificate
authority (see Certificate Procedures on page 46).
The browser must be configured to trust that certificate authority (beyond the scope of this
documentation).
If trust can’t be established, most browsers allow connection anyway, but display a ‘nag’ dialog to the
user, requesting permission.
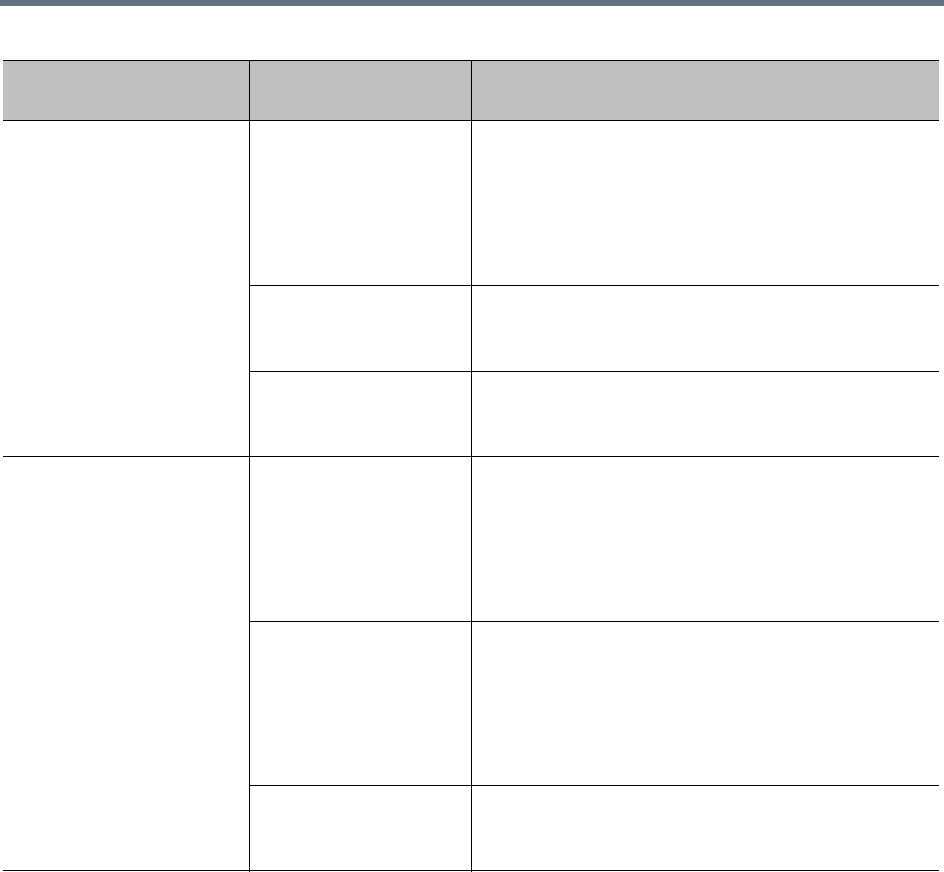
Encoding
Protocol /
File Type Description and Installation Method
PEM (Base64-encoded
ASCII text)
PKCS #7 protocol
P7B file
Certificate chain containing:
• A signed certificate for the system, authenticating its
public key.
• The CA’s public certificate.
• Sometimes intermediate certificates.
Upload file or paste into text box.
CER (single certificate)
file
Signed certificate for the system, authenticating its
public key.
Upload file or paste into text box.
Certificate text Encoded certificate text copied from CA’s email or
secure web page.
Paste into text box.
DER
(binary format using ASN.1
Distinguished Encoding
Rules)
PKCS #12 protocol
PFX file
Certificate chain containing:
• A signed certificate for the system, authenticating its
public key.
• A private key for the system.
• The CA’s public certificate.
Upload file.
PKCS #7 protocol
P7B file
Certificate chain containing:
• A signed certificate for the system, authenticating its
public key.
• The CA’s public certificate.
• Sometimes intermediate certificates.
Upload file.
CER (single certificate)
file
Signed certificate for the system, authenticating its
public key.
Upload file.


















