DMA Operations Guide Signaling Settings
68 Polycom, Inc.
Either H.323 signaling, SIP signaling, or both must be enabled in order for the
Polycom DMA system’s Conference Manager to receive calls for multipoint
conferences (virtual meeting rooms, or VMRs) and distribute them among its
pool of MCUs.
XMPP Signaling
If XMPP signaling is enabled, the Polycom DMA system’s Call Server operates
as an XMPP server, providing chat and presence services to the XMPP clients
that log into it.
Logins are accepted from any DMA user, local or Active Directory. Clients log
in by sending an XMPP login message to the virtual signaling address (IP or
FQDN) and XMPP port number of the DMA system, such as:
dma1.polycom.com:5223
Logged-in clients have presence and chat capability amongst themselves and
with clients logged into any federated XMPP service. Federation is automatic
and depends simply on DNS resolution of domains.
See xmpp.org for more information.
The following table describes the fields on the Signaling Settings page.
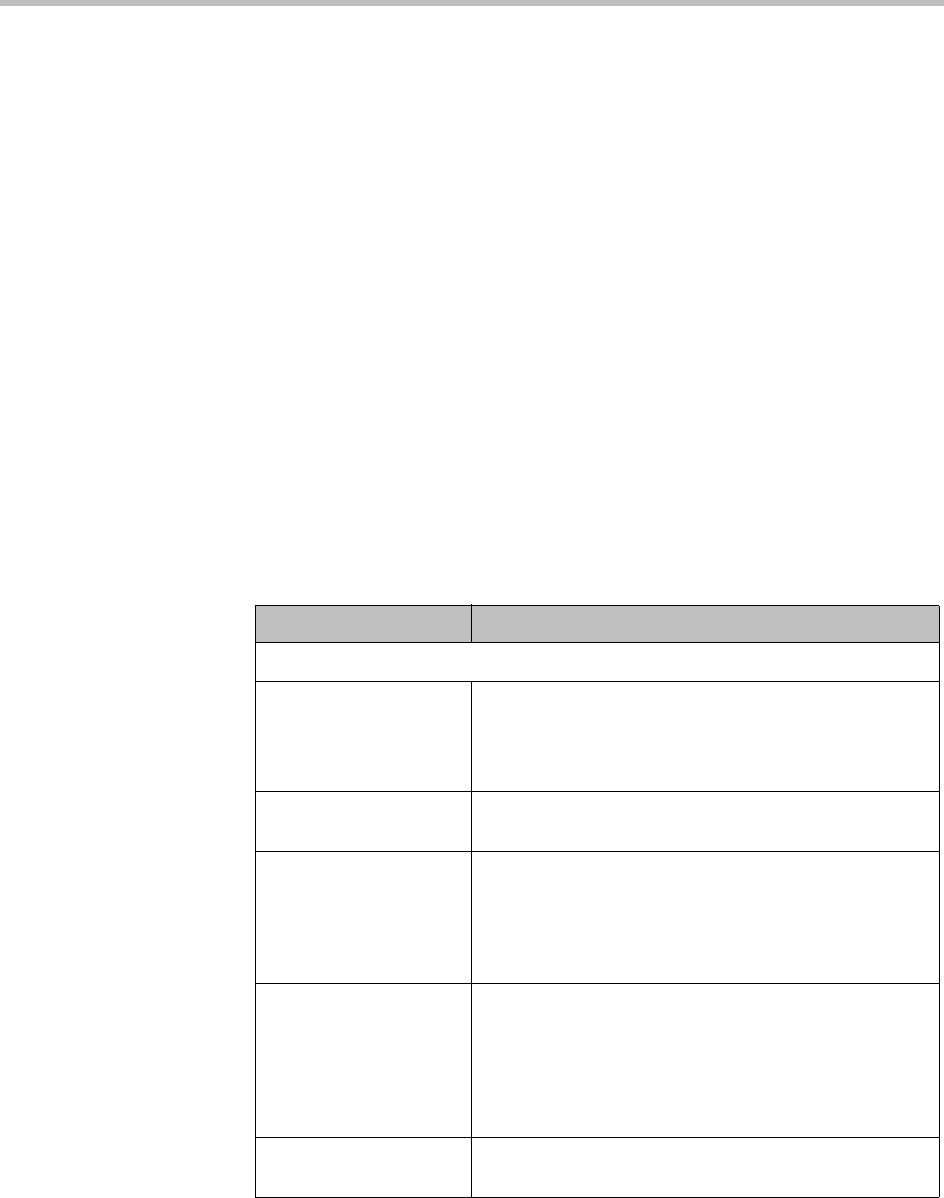
Table 4-5 Fields on the Signaling Settings page
Field Description
H.323 Settings
Enable H.323 signaling Enables the system to receive H.323 calls.
Caution: Disabling H.323 terminates any existing H.323
calls. When you click Update, the system prompts you
to confirm.
Status Indicates whether the system’s H.323 gatekeeper
functions are active.
H.225 port Specifies the port number the system’s gatekeeper uses
for call signaling.
We recommend using the default port number (1720),
but you can use any value from 1024 to 65535 that’s not
already in use and is different from the RAS port.
RAS port Specifies the port number the system’s gatekeeper uses
for the RAS (Registration, Admission and Status)
channel.
We recommend using the default port number (1719),
but you can use any value from 1024 to 65535 that’s not
already in use and is different from the H.225 port.
H.245 open firewall
ports
Shows the port range used for H.245 so you can
configure your firewall accordingly. This is display only.


















