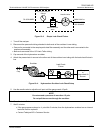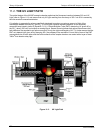
Teledyne API M100E Analyzer Operation Manual Theory Of Operation
223
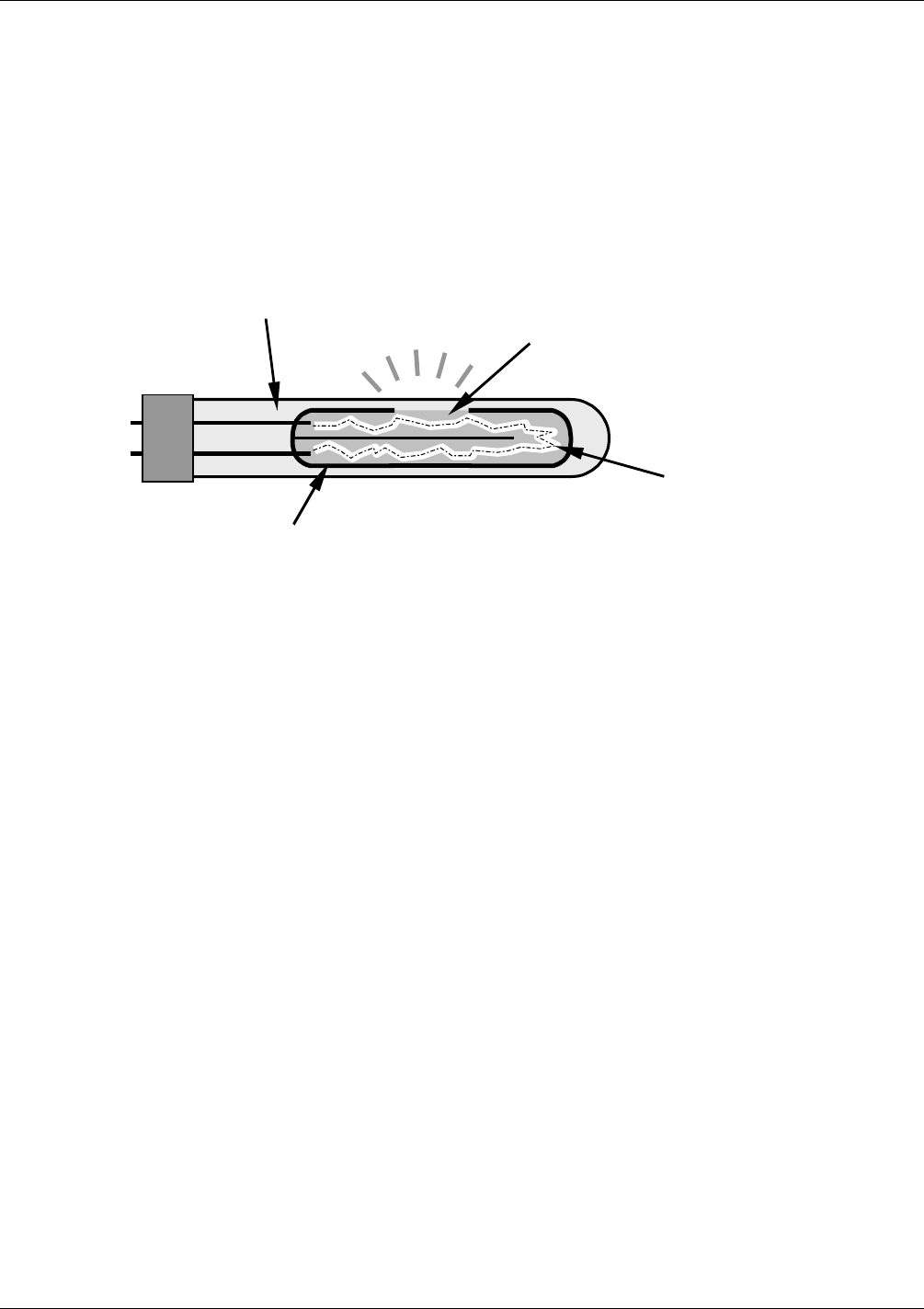
11.2.1. UV SOURCE LAMP
The source of excitation UV light for the M100E is a low pressure zinc-vapor lamp. An AC voltage heats up and
vaporizes zinc contained in the lamp element creating a light-producing plasma arc. Zinc-vapor lamps are
preferred over the more common mercury-vapor lamps for this application because they produce very strong
emission levels at the wavelength required to convert SO
2
to SO
2
*, 213.9 nm (refer to Figure 11-4).
The lamp used in the M100E is constructed with a vacuum jacket surrounding a double-bore lamp element (refer
to Figure 11-3). The vacuum jacket isolates the plasma arc from mo
st external temperature fluctuations. The
jacket also contains thermal energy created by the lamp’s operation therefore helping the lamp to heat up and
maintain proper vaporization temperature. Light is emitted through a 20 mm x 5 mm portal.
Li
g
ht Output
Portal
Zinc-
V
apor
Plasma Arc
V
acuum
Jacket
Dual Bore
Figure 11-3: Source UV Lamp Construction
11.2.2. THE REFERENCE DETECTOR
A vacuum diode, UV detector that converts UV light to a DC current is used to measure the intensity of the
excitation UV source lamp. It is located directly across from the source lamp at the back of a narrow tube-shaped
light trap, which places it directly in the path of the excitation UV light. A window transparent to UV light provides
an air-proof seal that prevents ambient gas from contaminating the sample chamber. The shape of the light trap
and the fact that the detector is blind to wavelengths other than UV no extra optical filtering is needed.
11.2.3. THE PMT
The amount of fluoresced UV produced in the sample chamber is much less than the intensity of excitation UV
source lamp (refer to Figure 11-4). Therefore a much more sensitive device is
needed to detect this light with
enough resolution to be meaningful. The M100E uses a Photo Multiplier Tube or PMT for this purpose.
A PMT is typically a vacuum tube containing a variety of specially designed electrodes. Photons enter the PMT
and strike a negatively charged photo cathode causing it to emit electrons. These electrons are accelerated by a
high voltage applied across a series of special electrodes called dynodes that multiply the amount of electrons
until a useable current signal is generated. This current increases or decreases with the amount of detected light
(refer to Section 11.4.3 for more details regarding the electroni
c op
eration of the PMT).
11.2.4. UV LAMP SHUTTER & PMT OFFSET
Inherent in the operation of both the reference detector and the PMT are a minor electronic offsets. The degree
of offset differs from detector to detector and from PMT to PMT and can change over time as these components
age.
To account for these offsets the M100E includes a shutter, located between the UV Lamp and the source filter
that periodically cuts off the UV light from the sample chamber. This happens every 30 minutes. The analyzer
records the outputs of both the reference detector and the PMT during this dark period and factors them into the
SO
2
concentration calculation.
04515F DCN6048