10-1
CHAPTER 10
PULSE-WIDTH MODULATOR
The pulse-width modulator (PWM) module has two output pins, each of which can output a
PWM signal with a fixed, programmable frequency and a variable duty cycle. These outputs can
be used to drive motors that require an unfiltered PWM waveform for optimal efficiency, or they
can be filtered to produce a smooth analog signal.
This chapter provides a functional overview of the pulse-width modulator module, describes how
to program it, and provides sample circuitry for converting the PWM outputs to analog signals.
For detailed descriptions of the signals and registers discussed in this chapter, please refer to Ap-
pendix B, “Signal Descriptions” and Appendix C, “Registers.”
10.1 PWM FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
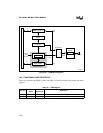
The PWM module has two channels, each of which consists of a control register
(PWMx_CONTROL), a buffer, a comparator, an RS flip-flop, and an output pin. Two other com-
ponents, an eight-bit counter (PWM_COUNT) and a period register (PWM_PERIOD), are
shared across the PWM module’s two channels, completing the circuitry (see Figure 10-1).