C-41
REGISTERS
PSW
12 VT Overflow-trap Flag
This flag is set when the overflow flag is set, but it is cleared only by the
CLRVT, JVT, and JNVT instructions. This allows testing for a possible
overflow at the end of a sequence of related arithmetic operations, which
is generally more efficient than testing the overflow flag after each
operation.
11 C Carry Flag
This flag is set to indicate an arithmetic carry or the last bit shifted out of
an operand. It is cleared if a subtraction operation generates a borrow.
Normally, the result is rounded up if the carry flag is set. The sticky bit
flag allows a finer resolution in the rounding decision. (See the PSW flag
descriptions in Appendix A for details.)
10 PSE PTS Enable
This bit globally enables or disables the peripheral transaction server
(PTS). The EPTS instruction sets this bit; DPTS clears it.
0 = disable PTS
1 = enable PTS
9 I Interrupt Disable (Global)
This bit globally enables or disables the servicing of all
maskable
interrupts
. The bits in INT_MASK and INT_MASK1 individually enable or
disable the interrupts. The EI instruction sets this bit; DI clears it.
0 = disable interrupt servicing
1 = enable interrupt servicing
8 ST Sticky Bit Flag
This flag is set to indicate that, during a right shift, a “1” was shifted into
the carry flag and then shifted out. It can be used with the carry flag to
allow finer resolution in rounding decisions.
PSW (Continued)
no direct access
The processor status word (PSW) actually consists of two bytes. The high byte is the status word,
which is described here; the low byte is the INT_MASK register. The status word contains one bit
(PSW.1) that globally enables or disables servicing of all maskable interrupts, one bit (PSW.2) that
enables or disables the peripheral transaction server (PTS), and six Boolean flags that reflect the
state of a user’s program.
The status word portion of the PSW cannot be accessed directly. To access the status word, push the
value onto the stack (PUSHF), then pop the value to a register (POP
test_reg
). The PUSHF and
PUSHA instructions save the PSW in the system stack and then clear it; POPF and POPA restore it.
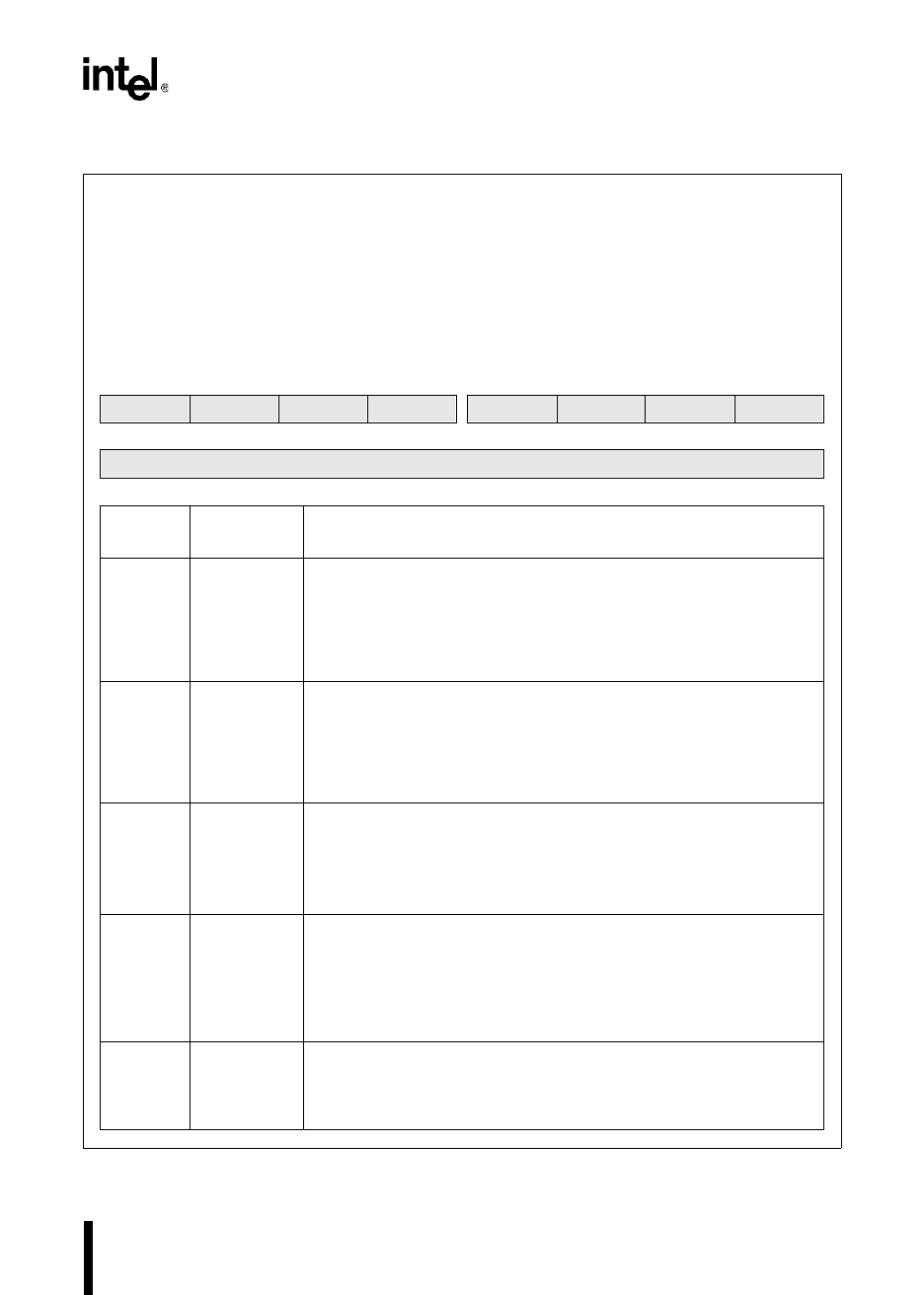
15 8
Z N V VT C PSE I ST
7 0
See INT_MASK on page C-25
Bit
Number
Bit
Mnemonic
Function


















