5-27
STANDARD AND PTS INTERRUPTS
5.6.2 Selecting the PTS Mode
The second byte of each PTSCB is always an 8-bit value called PTSCON. Bits 5–7 select the PTS
mode (Figure 5-15). The function of bits 0–4 differ for each PTS mode. Refer to the sections that
describe each mode in detail to see the function of these bits. Table 5-4 on page 5-12 lists the cycle
execution times for each PTS mode.
5.6.3 Single Transfer Mode
In single transfer mode, an interrupt causes the PTS to transfer a single byte or word (selected by
the BW bit in PTSCON) from one memory location to another. This mode is typically used with
the EPA to move captured time values from the event-time register to internal RAM for further
processing. See AP-483, Application Examples Using the 8XC196MC/MD Microcontroller, for
application examples with code. Figure 5-16 shows the PTS control block for single transfer
mode.
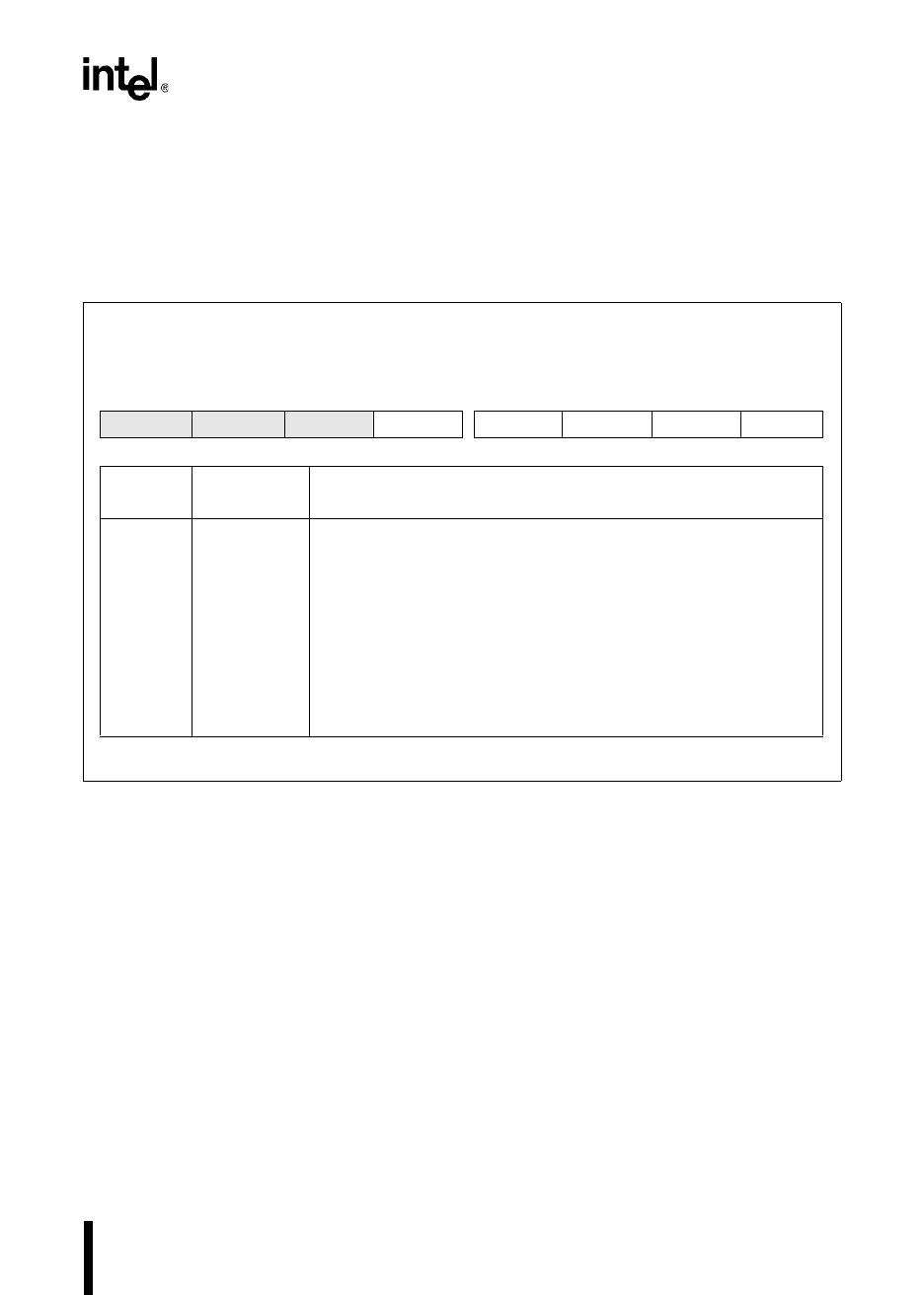
PTSCON
Address: PTSPCB + 1
The PTS control (PTSCON) register selects the PTS mode and sets up control functions for that
mode.
7 0
M2 M1 M0
†††††
Bit
Number
Bit
Mnemonic
Function
7:5 M2:0 PTS Mode
These bits select the PTS mode:
M2 M1 M0
000block transfer
001serial receive (MC, MD only)
010reserved
011serial transmit (MC, MD only)
100single transfer
101reserved
110A/D scan
111reserved
†
The function of this bit depends upon which mode is selected. See the PTS control block description
in each PTS mode section.
Figure 5-15. PTS Mode Selection Bits (PTSCON Bits 7:5)


















