8XC196MC, MD, MH USER’S MANUAL
16-8
16.4 PROGRAMMING PULSE WIDTH
The programming pulse width is controlled in different ways, depending on the programming
mode. In slave programming mode, the pulse width is controlled by the PALE# signal. In auto
programming mode, it is loaded from the external EPROM into the PPW register. In the UPROM
(8XC196MH only) and PCCB programming modes, the pulse width is controlled by the test-
ROM routine. (For run-time programming, your software controls the pulse width.)
To determine the correct PPW_VALUE for the frequency of the device, use the following formula
and round the result to the next higher integer.
where:
PPW_VALUE is a 16-bit word
F
XTAL1
is the input frequency on XTAL1, in MHz
The examples in Table 16-5 calculate the required minimum pulse width (100 µs for the
8XC196MH and 250 µs for the 8XC196MC, MD) for an 8-MHz and a 16-MHz crystal.
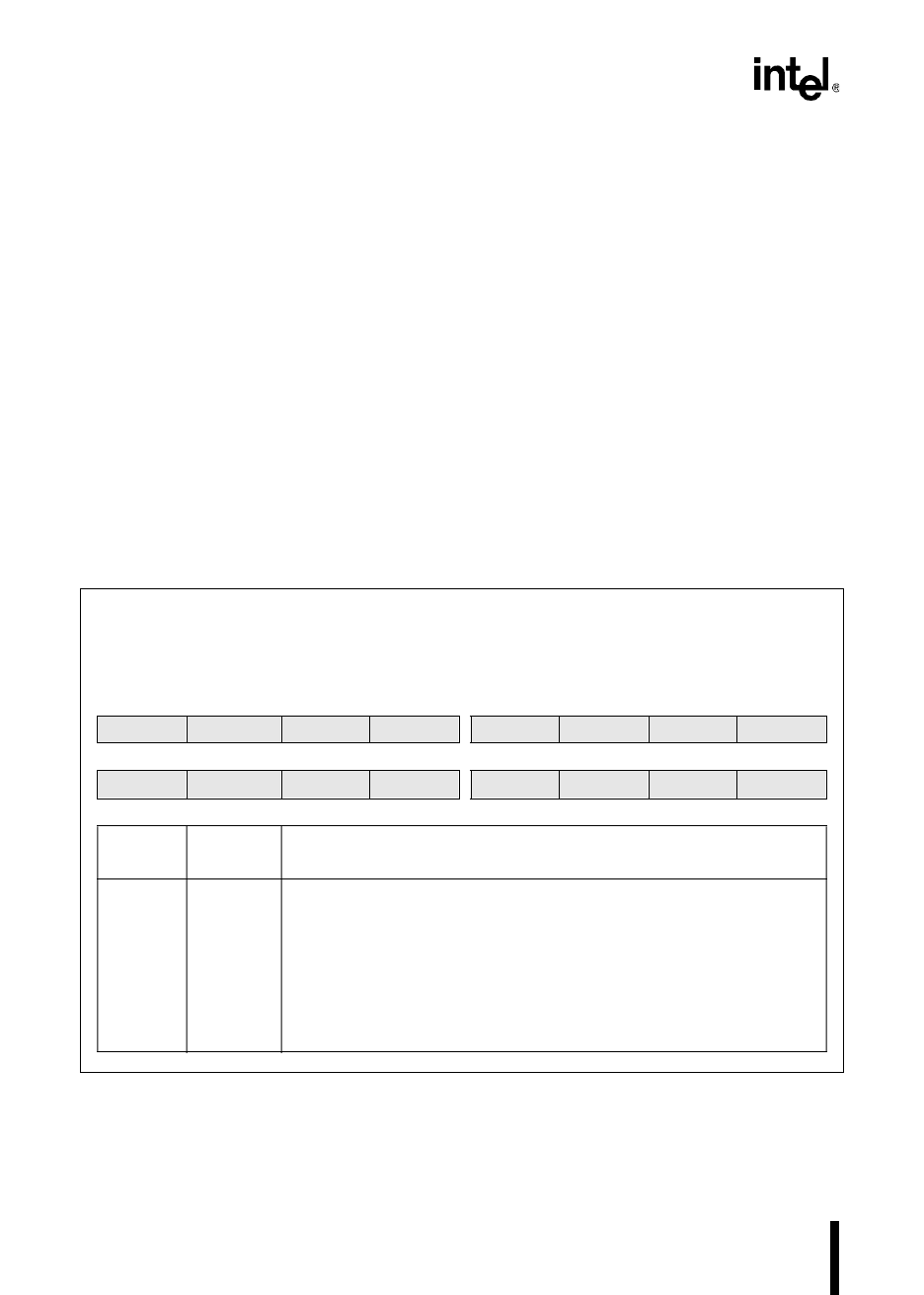
PPW
no direct access
The programming pulse width (PPW) register is loaded from the external EPROM (locations 14H and
15H for the 8XC196MC and MD; locations 4014H and 4015H for the 8XC196MH) in auto programming
mode. The PPW_VALUE determines the programming pulse width.
15 8
PPW15 PPW14 PPW13 PPW12 PPW11 PPW10 PPW9 PPW8
7 0
PPW7 PPW6 PPW5 PPW4 PPW3 PPW2 PPW1 PPW0
Bit
Number
Bit
Mnemonic
Function
15:0 PPW15:0 PPW_VALUE
This value establishes the programming pulse width for auto programming.
Use the appropriate formula to calculate the PPW_VALUE, then write the
result to the PPW register. (Table 16-5 shows the calculations and results for
8 MHz and 16 MHz operation.)
Figure 16-2. Programming Pulse Width (PPW) Register
PPW_VALUE for 8XC196MC, MD 62.5 F
XTAL1
×
PPW_VALUE for 8XC196MH = 25 F
XTAL1
×
=
PPW_VALUE for 8XC196MC, MD 62.5 F
XTAL1
×
PPW_VALUE for 8XC196MH = 25 F
XTAL1
×
=