16-9
PROGRAMMING THE NONVOLATILE MEMORY
16.5 MODIFIED QUICK-PULSE ALGORITHM
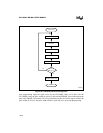
Both the slave and auto programming routines use the modified quick-pulse algorithm (Figure
16-3). The modified quick-pulse algorithm sends programming pulses to each OTPROM word
location. After the required number of programming pulses, a verification routine compares the
contents of the programmed location to the input data. A verification error deasserts the PVER
signal, but does not stop the programming routine. This process repeats until each OTPROM
word has been programmed and verified. Intel guarantees lifetime data retention for a device pro-
grammed with the modified quick-pulse algorithm.
NOTE
The 87C196MC, MD devices use two pulses; the 87C196MH uses five.
Table 16-5. Example PPW_VALUE Calculations
F
XTAL1
8XC196MC, MD
(Two 250-µs pulses required)
8XC196MH
(Five 100-µs pulses required)
8 MHz PPW_VALUE = 62.5 × 8 = 504 = 01F4H PPW_VALUE = 25 × 8 = 200 = 00C8H
16 MHz PPW_VALUE = 62.5 × 16 = 1000 = 03F8H PPW_VALUE = 25 × 16 = 400 = 0190H