16-17
PROGRAMMING THE NONVOLATILE MEMORY
16.8.3 Operating Environment
The chip configuration registers (CCRs) define the system environment. Since the programming
environment is not necessarily the same as the application environment, the device provides a
means for specifying different configurations. Specify your application environment in the chip
configuration bytes (CCBs) located in the OTPROM. Specify your programming environment in
the programming chip configuration bytes (PCCBs) located in the test ROM.
Figure 16-6 shows an abbreviated description of the CCRs with the default PCCB environment
settings. The reset sequence loads the CCRs from the CCBs for normal operation and from the
PCCBs when entering programming modes. You can program the CCBs using any of the pro-
gramming methods, but only slave mode allows you to program the PCCBs. Chapter 15, “Inter-
facing with External Memory,” describes the system configuration options, and “Controlling
Access to Internal Memory” on page 16-3 describes the memory protection options.
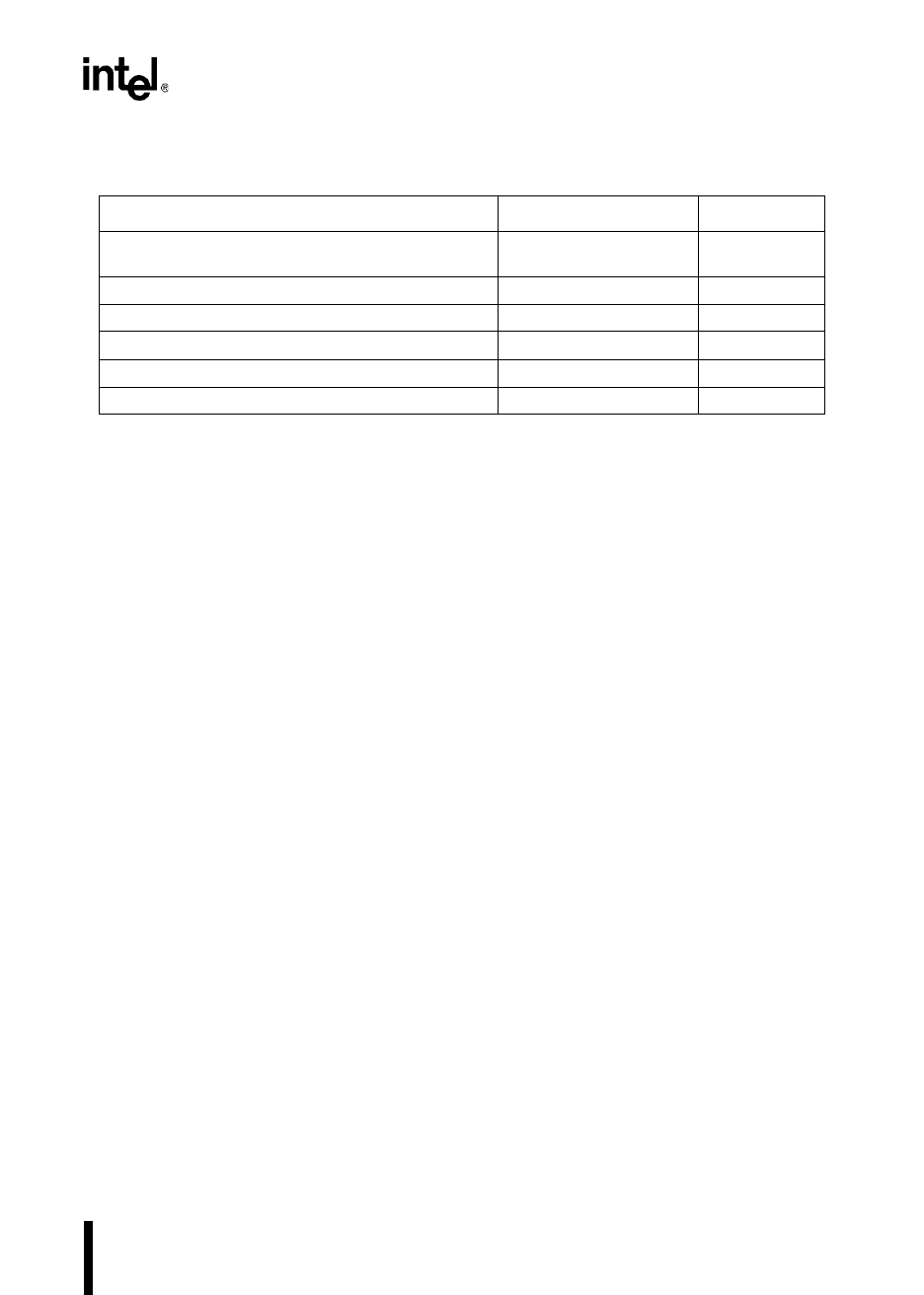
Table 16-9. Slave Programming Mode Memory Map
Description Address Comments
OTPROM (MH) 2000–9FFFH
(MC, MD) 2000–5FFFH
OTPROM Cells
DED
†
0758H UPROM Cell
DEI
†
0718H UPROM Cell
PCCB 0218H Test EPROM
Programming voltages (see Table 16-8 on page 16-16) 0072H, 0073H Read Only
Signature word 0070H Read Only
†
These bits program the UPROM cells. Once these bits are programmed, they cannot be erased and
dynamic failure analysis of the device is impossible.