Fortinet 454 FortiWeb 5.0 Patch 6 Administration Guide
14.Click OK.
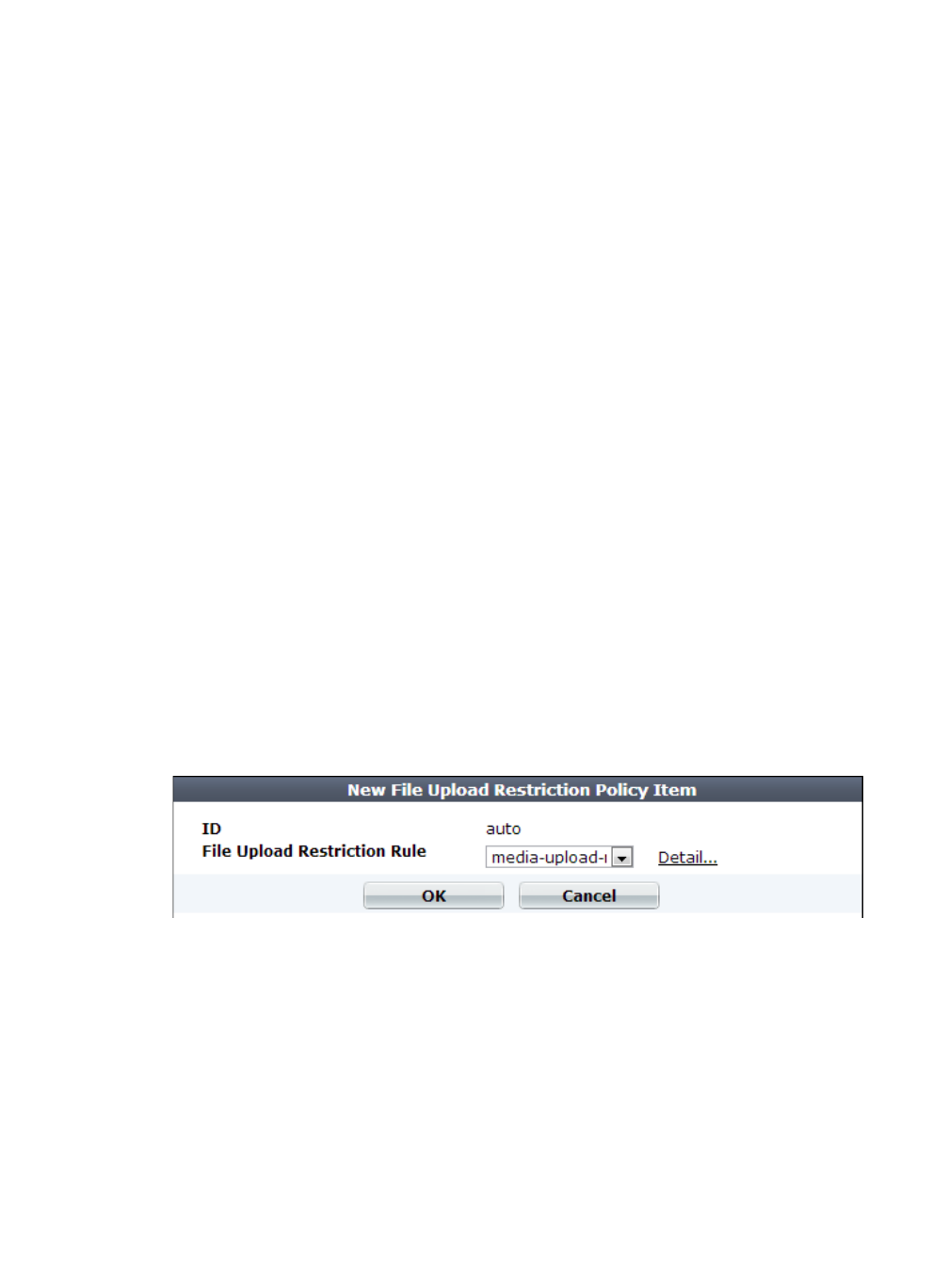
15.Click Create New to include a rule in the set.
A dialog appears.
16.From the File Upload Restriction Rule drop-down list, select an existing file upload restriction
rule that you want to use in the policy.
To view or change the information associated with the item, select the Detail link. The File
Upload Restriction Rule dialog appears. Use the browser Back button to return.
17.Click OK.
18.Repeat the previous steps for each rule that you want to add to the file upload restriction
policy.
19.To apply the file upload restriction policy, select it in an inline or offline protection profile (see
“Configuring a protection profile for inline topologies” on page 468 or “Configuring a
protection profile for an out-of-band topology or asynchronous mode of operation” on
page 477).
Block Period Type the number of seconds that you want to block subsequent
requests from the client after the FortiWeb appliance detects that the
client has violated the rule.
This setting is available only if Action is set to Period Block. The valid
range is from 1 to 3,600 (1 hour). The default value is 1. See also
“Monitoring currently blocked IPs” on page 606.
Severity When rule violations are recorded in the attack log, each log message
contains a Severity Level (severity_level) field. Select which
severity level the FortiWeb appliance will use when it logs a violation
of the rule:
•Low
•Medium
•High
The default value is High.
Trigger Action Select which trigger, if any, that the FortiWeb appliance will use when
it logs and/or sends an alert email about a violation of the rule. See
“Configuring triggers” on page 557.
Antivirus Scan Enable to scan for trojans. Also enable the signatures (Trojans) and
configure the antivirus-specific Action, Block Period, Severity, and
Trigger Action (see “Blocking known attacks & data leaks” on
page 387).
Attackers often modify HTTP header so that the request’s
Content-Type: does not match — it indicates an allowed file type,
but the byte code contained in the body is actually a virus. This scan
ensures that the request actually contains the file type that it
professes, and that it is not infected.


















