Fortinet 202 FortiWeb 5.0 Patch 6 Administration Guide
protection and maintenance features you can use. For details, see the other chapters in this
Administration Guide.
Reducing false positives
If the dashboard indicates that you are getting dozens or hundreds of nearly identical attacks,
they may actually be legitimate requests that were mistakenly identified as attacks (i.e. false
positives). Many of the signatures, rules, and policies that make up protection profiles are
based, at least in part, on regular expressions. If your web sites’ inputs and other values are
hard for you to predict, the regular expression may match some values incorrectly. If the
matches are not exact, many of your initial alerts may not be real attacks or violations. They will
be false positives.
Fix false positives that appear in your attack logs so that you can focus on genuine attacks.
Here are some tips:
• Examine your web protection profile (go to Policy > Web Protection Profile and view the
settings in the applicable offline or inline protection profile). Does it include a signature set
that seems to be causing alerts for valid URLs. If so, disable the signature to reduce false
positives.
• If your web protection profile includes a signature set where the Extended Signature Set
option is set to Full, reduce it to Basic to see if that reduces false positives. See “Specifying
URLs allowed to initiate sessions” on page 415.
• If your web protection profile includes HTTP protocol constraints that seem to be causing
alerts for legitimate HTTP requests, create and use exceptions to reduce false positives. See
“Configuring HTTP protocol constraint exceptions” on page 446.
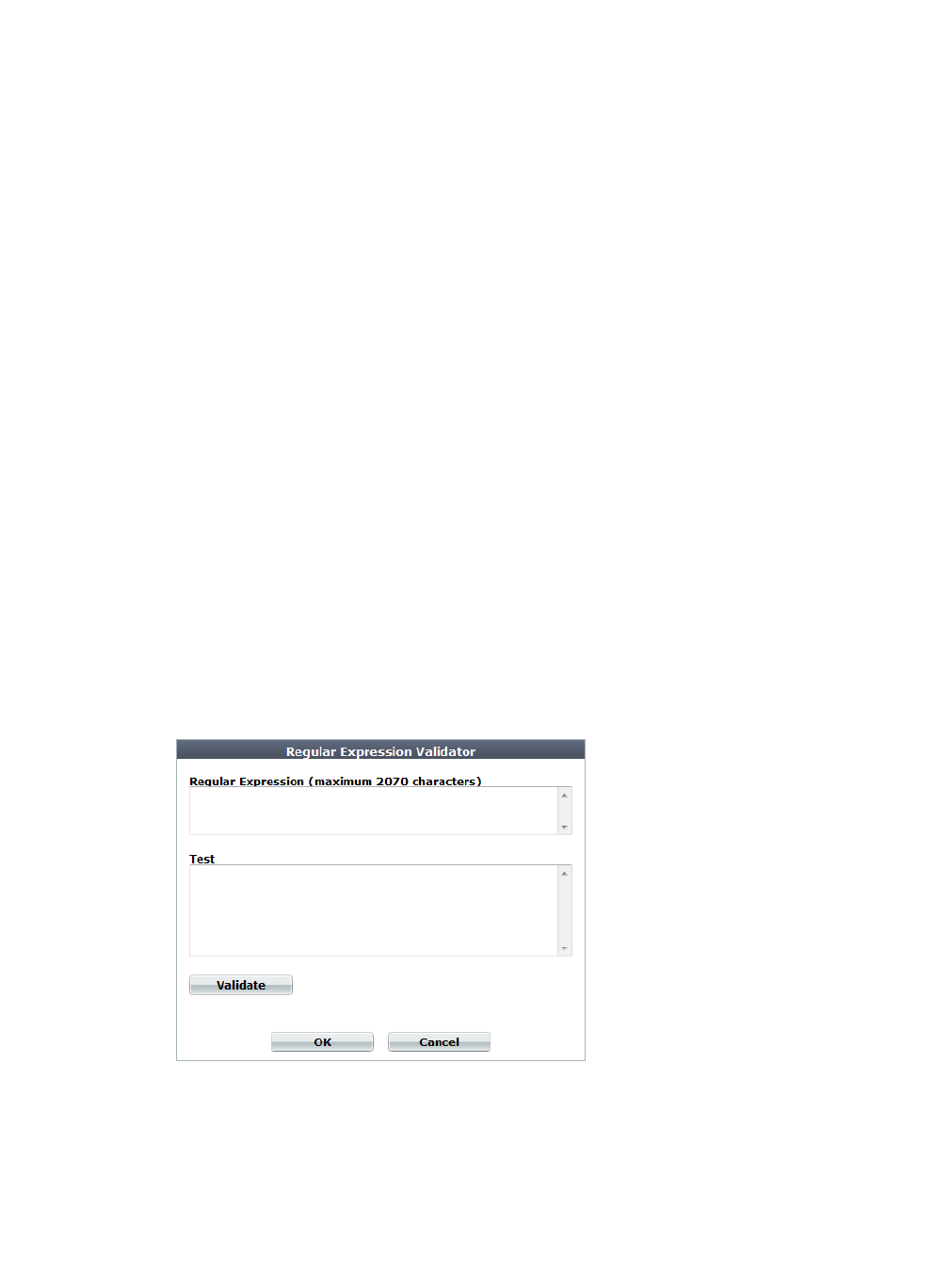
• Most dialog boxes that accept regular expressions include the >> (test) icon. This opens the
Regular Expression Validator window, where you can fine-tune the expression to eliminate
false positives.
Figure 29:Regular Expression Validator dialog
• If you use features on the DoS Protection menu to guard against denial-of-service attacks,
you could have false positives if you set the thresholds too low. Every client that accesses a
web application generates many sessions as part of the normal process. Try adjusting some
thresholds higher.
• To learn more about the behavior of regular expressions that generate alerts, enable the
Retain Packet Payload options in the logging configuration. Packet payloads provide the
actual data that triggered the alert, which may help you to fine tune your regular expressions
to reduce false positives. See “Enabling log types, packet payload retention, & resource
shortage alerts” on page 546 and “Viewing log messages” on page 557.