Fortinet 278 FortiWeb 5.0 Patch 6 Administration Guide
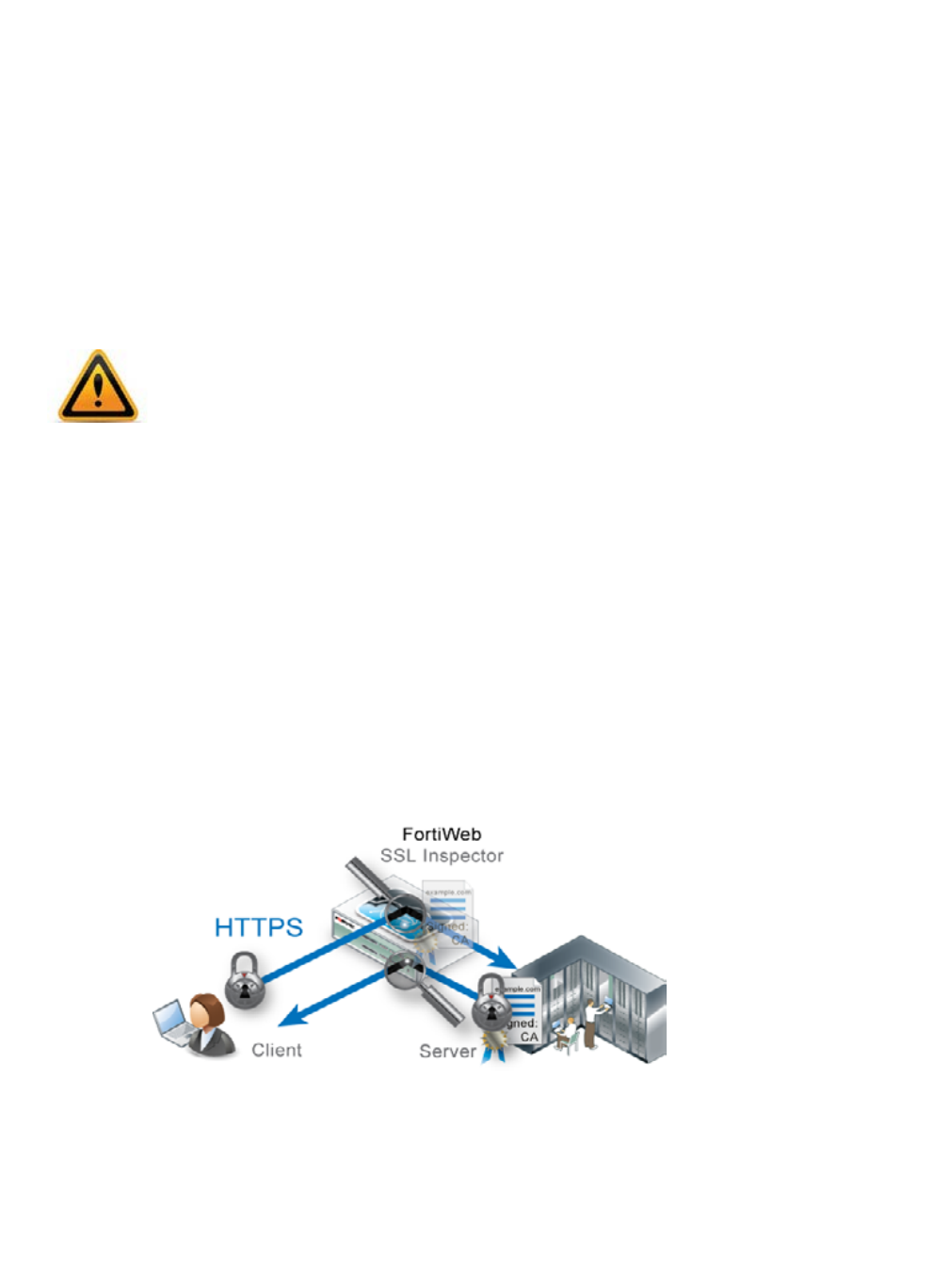
When SSL offloading, the web server does not use its own server certificate. Instead,
FortiWeb acts like an SSL proxy for the web server, possessing the web server’s certificate and
using it to:
• authenticate itself to clients
• decr
ypt requests
• encrypt responses
whenever a client requests an HTTPS connection to that web server.
As a side effect of being an SSL terminator, the FortiWeb is in possession of both the HTTP
r
eque
st and reply in their decrypted state. Because they are not encrypted at that point on the
path, FortiWeb can rewrite content and/or route traffic based upon the contents of Layer 7 (the
application layer). Otherwise Layer 7 content-based routing and rewriting would be impossible:
that part of the packets would be encrypted and unreadable to FortiWeb.
However, depending on the oper
ation
mode, FortiWeb is not always an SSL terminator.
By their asynchronous nature, SSL termination cannot be supported in transparent inspection
and of
fline protection modes. (To terminate, FortiWeb must process traffic synchronously with
the connection state.) In those modes, the web server uses its own certificate, and acts as
its own SSL terminator. The web server bears the load for SSL processing. FortiWeb only
“listens in” and can interrupt the connection, but otherwise cannot change or reroute packets.
In those modes, FortiWeb only uses the web server’s certificate to decrypt traffic in order to
scan it
for policy violations. If there are no violations, it allows the existing encrypted traffic to
continue without interruption. FortiWeb does not expend CPU and resources to re-encrypt,
because it is not a terminator.
In other words, FortiWeb performs SSL inspection, not SSL of
floading.
See also
• Supported cipher suites & protocol versions
• How to offload or inspect HTTPS
• How to offload or inspect HTTPS
Secure traffic between FortiWeb and back-end servers when using SSL offloading. Failure to do
so will compromise the security of all offloaded sessions. No attack will be apparent to clients,
as SSL offloading cannot be detected by them, and therefore they will not receive any alerts
that their session has been compromised.
For example, you might pass decrypted traffic to back-end servers as directly as possible,
through one switch that is physically located in the same locked rack, and that has no other
connections to the overall network.


















