Reference Manual
00809-0100-4665, Rev AA
August 2010
Rosemount 8732
C-12
Troubleshooting the
8714i Meter Verification
Test
In the event that the 8714i Meter Verification test fails, the following steps can
be used to determine the appropriate course of action. Begin by reviewing the
8714i results to determine the specific test that failed.
Figure C-1. Troubleshooting the
8714i Meter Verification Test
Table
8714i Meter Verification
Functionality
The 8714i Meter Verification diagnostic functions by taking a baseline sensor
signature and then comparing measurements taken during the verification
test to these baseline results.
Sensor Signature Values
The sensor signature describes the magnetic behavior of the sensor. Based
on Faraday’s law, the induced voltage measured on the electrodes is
proportional to the magnetic field strength. Thus, any changes in the magnetic
field will result in a calibration shift of the sensor. Having the transmitter take
an initial sensor signature when first installed will provide the baseline for the
verification tests that are done in the future. There are three specific
measurements that are stored in the transmitter’s non-volatile memory that
are used when performing the calibration verification.
Coil Circuit Resistance
The Coil Circuit Resistance is a measurement of the coil circuit health. This
value is used as a baseline to determine if the coil circuit is still operating
correctly when the 8714i Meter Verification diagnostic is initiated.
Coil Signature
The Coil Signature is a measurement of the magnetic field strength. This
value is used as a baseline to determine if a sensor calibration shift has
occurred when the 8714i Meter Verification diagnostic is initiated
Electrode Circuit Resistance
The Electrode Circuit Resistance is a measurement of the electrode circuit
health. This value is used as a baseline to determine if the electrode circuit is
still operating correctly when the 8714i Meter Verification diagnostic is
initiated.
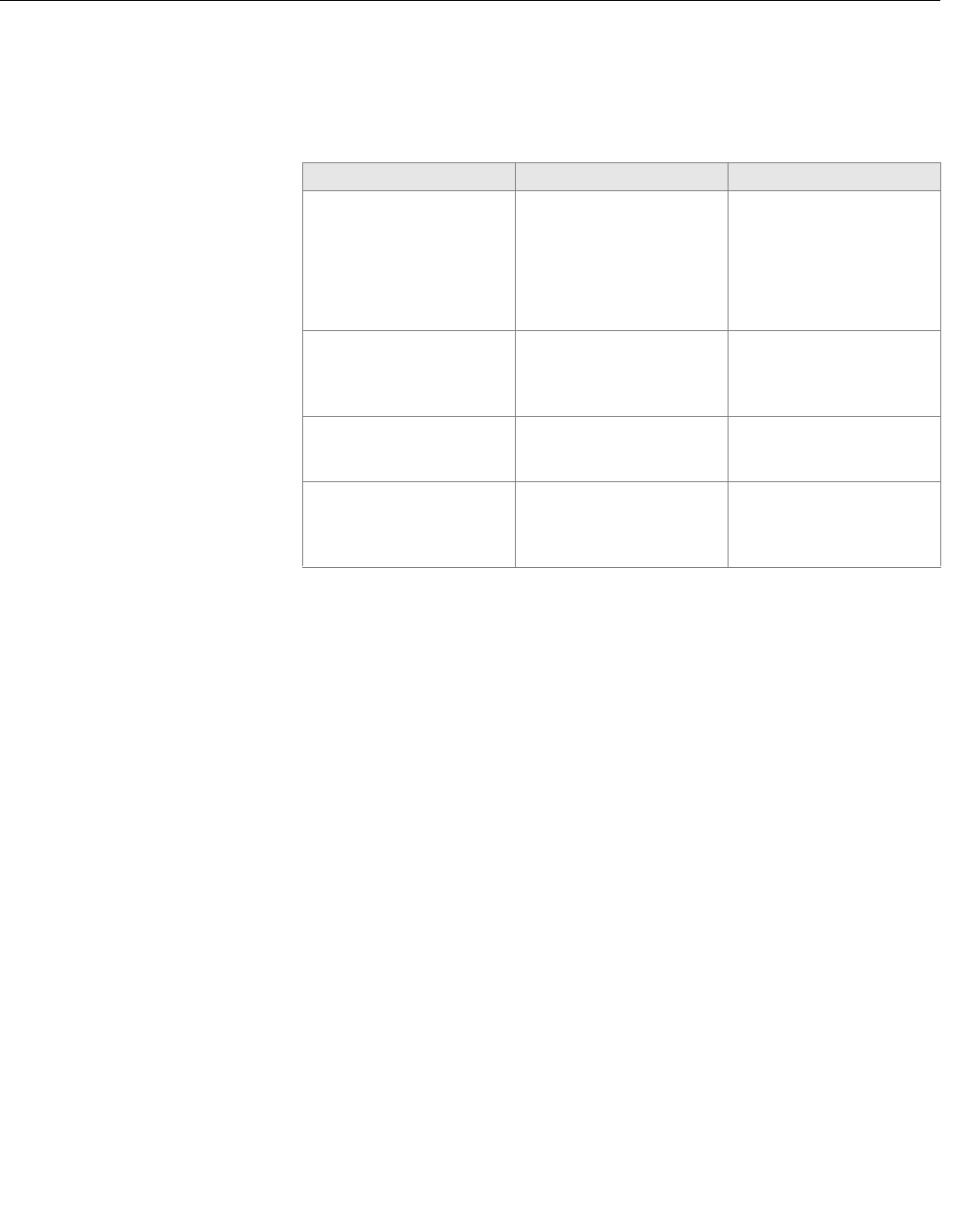
Test Potential Causes of Failure Steps to Correct
Transmitter Verification Test
Failed
• Unstable flow rate during
the verification test
• Noise in the process
• Transmitter drift
• Faulty electronics
• Perform the test with no
flow in the pipe
• Check calibration with an
external standard like the
8714D
• Perform a digital trim
• Replace the electronics
Sensor Verification Failed
• Moisture in the terminal
block of the sensor
• Calibration shift caused by
heat cycling or vibration
• Remove the sensor and
send back for recalibration.
Coil Circuit Health Failed
• Moisture in the terminal
block of the sensor
• Shorted Coil
• Perform the sensor checks
detailed on page 6-8.
Electrode Circuit Health
Failed
• Moisture in the terminal
block of the sensor
• Coated Electrodes
• Shorted Electrodes
• Perform the sensor checks
detailed on page 6-8.
