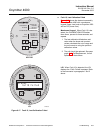
Instruction Manual
IB-106-340 Rev. 3.0
December 2003
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management Troubleshooting 8-21
Oxymitter 4000
3. Always note the time it takes for the
cell to recover to the normal process
value after the cal gas is removed. As
the diffuser plugs, this recovery time
will get longer and longer. Use the
Calibration Record form provided in
this manual.
Can I calibrate a badly plugged diffuser?
1. It may not be possible to immediately
replace a plugged diffuser while the
process is on line.
2. One can calibrate the probe without
pressurizing the cell by adjusting the
calibration gas flow rate downward
before calibration. For instance, say
the process is at 3%, and the first
calibration gas is 8%. Adjust the flow
of cal gas downward until the reading
begins to migrate from 8% to lower
values, indicating that process gases
are now mixing in with the calibration
gases.
3. Adjust the flow rate back up until this
mixing is just eliminated. Calibrate at
this flow rate. Replace the diffuser at
the first opportunity.
Install all protective equipment covers
and safety ground leads after trouble-
shooting. Failure to replace covers
and ground leads could result in seri-
ous injury or death.
8-7 SPS 4000 TROUBLESHOOTING
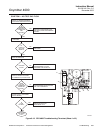
Use the CAL FAIL and IN CAL relay outputs to
identify possible SPS 4000 faults.
a. If a calibration was not successfully com-
pleted, the SPS 4000 sends a CAL FAIL
contact indication to the control room. To
determine if the SPS 4000 caused the failed
calibration, go to the Oxymitter 4000 site to
view the keypad. Or, access the HART/AMS
menus. For more information on
HART/AMS, refer to Section 7, HART/AMS.
1. If no alarms are indicated on the key-
pad or in the HART/AMS STATUS
sub-menu, the calibration did not fail
because of an Oxymitter 4000 fault.
Therefore, a calibration gas flow prob-
lem occurred. Refer to Table 8-3 or
Figure 8-19 to troubleshoot the SPS
4000.
2. If the LAST CAL FAILED alarm is indi-
cated on the keypad or in the HART/
AMS STATUS sub-menu, the failure is
due to either a bad Oxymitter 4000 cell
or a calibration gas flow problem.
(a) Verify your calibration setup per
paragraph 9-2 in Section 9, MAIN-
TENANCE AND SERVICE, Also,
verify your calibration gas setup.
(b) Perform another calibration and
monitor the process. If the calibra-
tion fails before both calibration
gases finish sequencing, a gas flow
problem exists. Refer to Table 8-3
or Figure 8-19 to troubleshoot the
SPS 4000.
If the calibration setup is correct
and the Oxymitter 4000 indicates
an invalid slope fault (fault 13) be-
fore the gases are purged and a
last calibration failed fault (fault 15)
after the gases are purged, replace
the Oxymitter 4000 cell per para-
graph 9-4i in Section 9, MAINTE-
NANCE AND SERVICE.
b. If a semi-automatic or manual calibration is
being performed but no 5 - 30 VDC relay
output contact (IN CAL or CAL FAIL) is be-
ing received by the control room, the inter-
face board relays are malfunctioning.
Replace the interface board per paragraph
9-5b.
NOTE
If the unit is performing frequent auto-
calibrations, investigate at the Oxymit-
ter 4000 site or using HART/AMS. This
condition may indicate an aging cell in
the Oxymitter 4000.