Net Oil Computer Supplement 11
NOC Overview
NOC Overview NOC ConfigurationUsing the DisplayBefore You Begin
2.3.3 Shrinkage factors
“Shrinkage” is a decrease in volume caused by the evaporation of solution gas, by the flashing of
volatile natural gas, or by lowered temperature during the crude oil stabilization process. By
estimating the shrinkage during oil storage or transport, you can estimate sellable oil based on
upstream volume measurement.
The NOC application includes two shrinkage factors: one for oil and one for water. The net oil flow
rate and net water flow rate measured by the NOC application are automatically multiplied by the
corresponding shrinkage factor. By default, the shrinkage factors are set to 1.0, resulting in no
compensation for shrinkage.
Use your standard methods to determine the appropriate shrinkage factors, taking into consideration
the location of the Micro Motion sensor in your process.
2.3.4 Gas carry-under – Transient Bubble Remediation (TBR)
Transient Bubble Remediation (TBR) is a standard feature of the NOC application. It is used to
provide more accurate process data during intermittent gas carry-under – gas entrainment in the liquid
stream. TBR is applicable only when the density-based water cut is used.
Note: If a water cut monitor is used to measure water cut directly, see the vendor documentation for
suggestions on maintaining accuracy through transient bubble conditions.
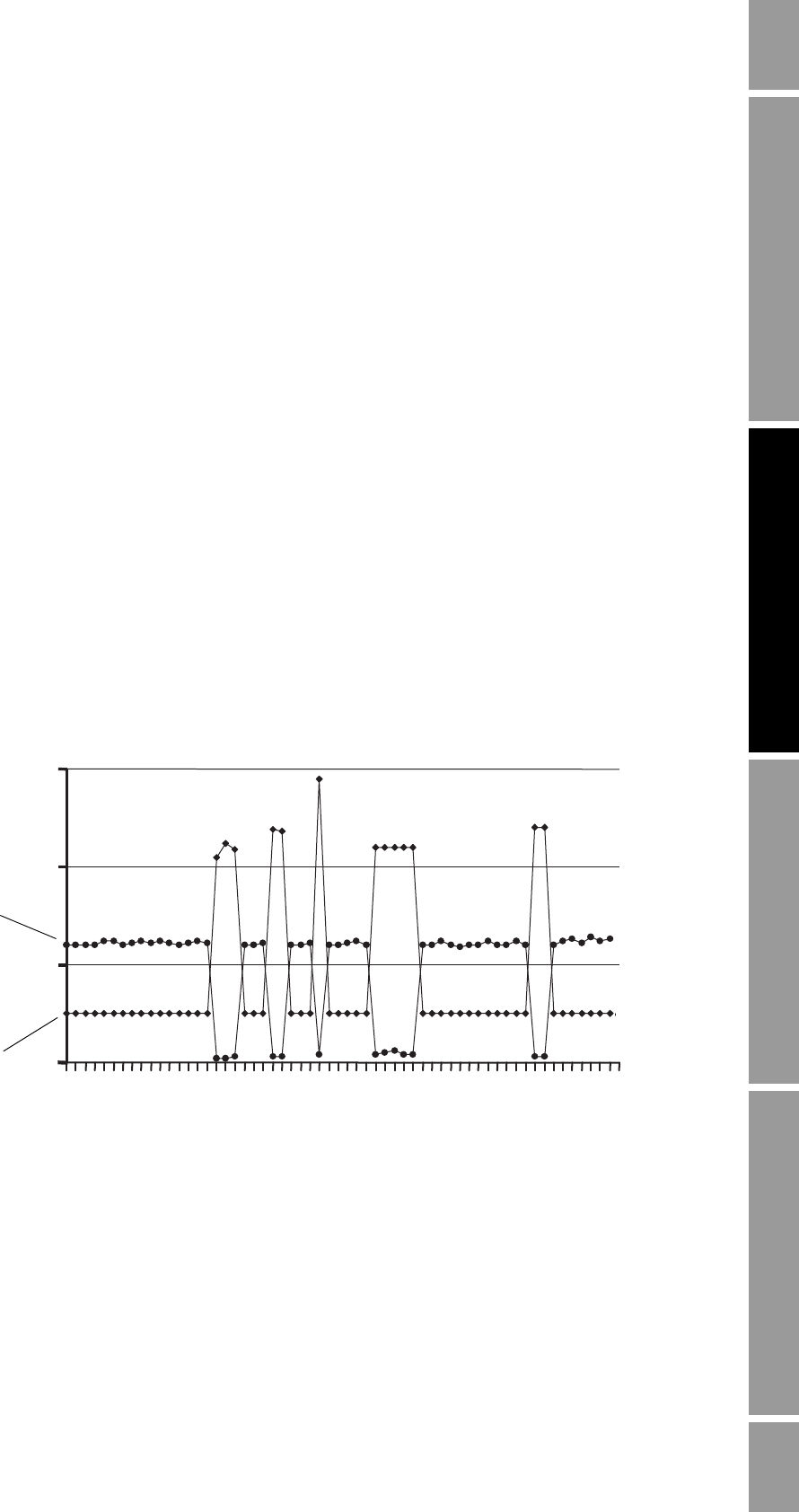
When the density-based water cut is used to calculate net oil, transient bubbles have a negative effect
on NOC measurement accuracy. Figure 2-6 shows the effect of transient bubbles on density.
Figure 2-6 Effect of transient bubbles on density
A “transient bubble condition” is defined in terms of the sensor’s drive gain: if the drive gain exceeds
the configured threshold for more than three seconds, the configured TBR actions are performed. The
transient bubble interval persists until drive gain is below the configured threshold for three seconds.
Drive gain (%)
Density (measured)
Drive gain (actual)


















