8XC196NP, 80C196NU USER’S MANUAL
13-10
Note that the 32-Kbyte address range could not have 4000H as base address, for example, because
4000H is not on a 32-Kbyte boundary.
“Example of a Chip-select Setup” on page 13-12 shows another example of setting up the chip-
select unit.
13.3.2 Controlling Wait States, Bus Width, and Bus Multiplexing
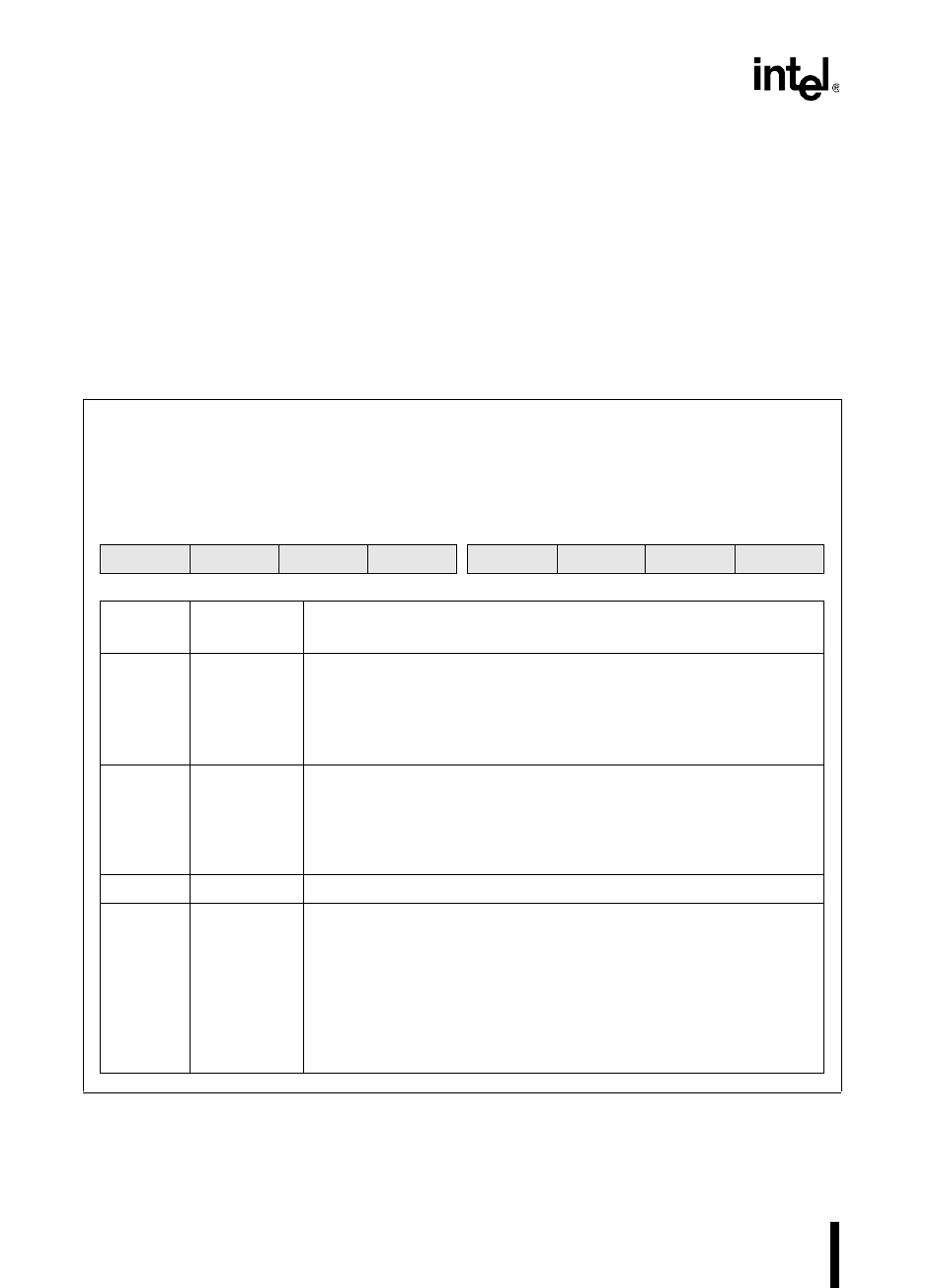
For each chip-select output address range, the bus control register BUSCONx (Figure 13-4) de-
termines the wait states, the bus width, and the address/data multiplexing.
BUSCON
x
x
= 0–5
Address:
Reset State:
Table 13-7
For the address range assigned to chip-select
x
, the bus control (BUSCON
x
) register specifies the
number of wait states, the bus width, and the address/data multiplexing for all external bus cycles that
access address range
x
.
7 0
DEMUX BW16 — — — — WS1 WS0
Bit
Number
Bit
Mnemonic
Function
7 DEMUX Address/Data Multiplexing
This bit specifies the address/data multiplexing on AD15:0 for all
external accesses to the address range assigned to chip-select
x
output.
0 = multiplexed
1 = demultiplexed
6 BW16 Bus Width
This bit specifies the bus width for all external accesses to the address
range assigned to chip-select
x
output.
0 = 8 bits
1 = 16 bits
5:2 — Reserved; for compatibility with future devices, write zeros to these bits.
1:0 WS1:0 Wait States
These bits specify the number of wait states for all external accesses to
the address range assigned to chip-select
x
output.
WS1 WS0 Wait States
00 0
01 1
10 2
11 3
Figure 13-4. Bus Control (BUSCON
x
) Register


















