8XC196NP, 80C196NU USER’S MANUAL
11-6
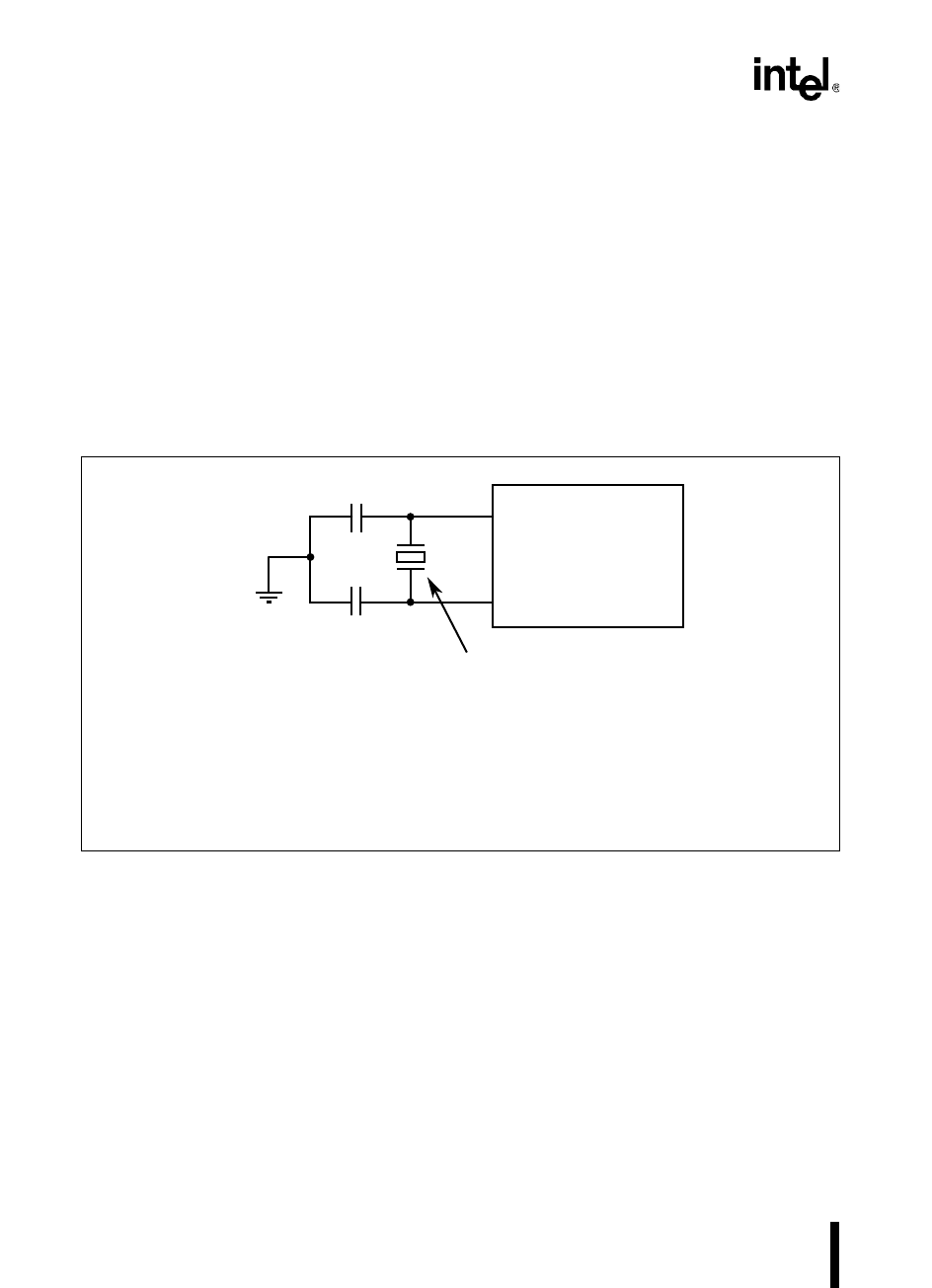
Figure 11-4 shows the connections between the external crystal and the device. When designing
an external oscillator circuit, consider the effects of parasitic board capacitance, extended oper-
ating temperatures, and crystal specifications. Consult the manufacturer’s datasheet for perfor-
mance specifications and required capacitor values. With high-quality components, 20 pF load
capacitors (C
L
) are usually adequate for frequencies above 1 MHz.
Noise spikes on the XTAL1 or XTAL2 pin can cause a miscount in the internal clock-generating
circuitry. Capacitive coupling between the crystal oscillator and traces carrying fast-rising digital
signals can introduce noise spikes. To reduce this coupling, mount the crystal oscillator and ca-
pacitors near the device and use short, direct traces to connect to XTAL1, XTAL2, and V
SS
. To
further reduce the effects of noise, use grounded guard rings around the oscillator circuitry and
ground the metallic crystal case.
Figure 11-4. External Crystal Connections
In cost-sensitive applications, you may choose to use a ceramic resonator instead of a crystal os-
cillator. Ceramic resonators may require slightly different load capacitor values and circuit con-
figurations. Consult the manufacturer’s datasheet for the requirements.
8XC196
Device
XTAL2
XTAL1
Quartz Crystal
C1
C2
A0273-02
Note:
Mount the crystal and capacitors close to the device using
short, direct traces to XTAL1, XTAL2, and V
ss
. When
using a crystal, C1=C2≈20 pF. When using a ceramic
resonator, consult the manufacturer for recommended
oscillator circuitry.