Appendices
22 Test Bed Receiver Subsystem Addendum – Rev 1
A WAAS OVERVIEW
The Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) is a safety-critical system which is designed to enable the GPS to meet
the US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) navigation performance requirements for domestic en route, terminal,
non-precision approach and precision approach phases of flight. The primary functions of WAAS include:
• data collection
• determining ionospheric corrections, satellite orbits, satellite clock corrections and satellite integrity
• independent data verification
• WAAS message broadcast and ranging
• system operations & maintenance
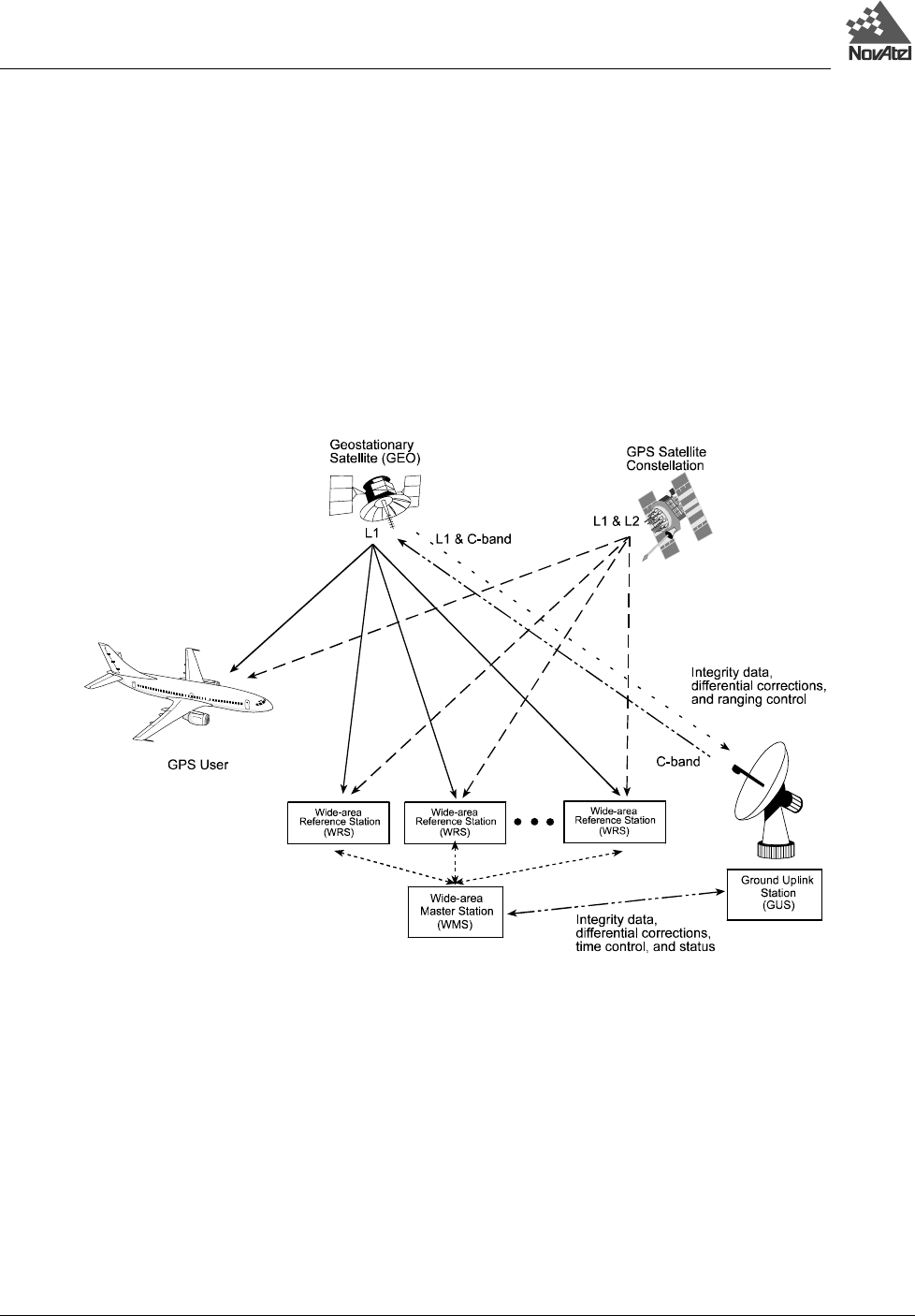
Figure 13 The WAAS Concept
As shown in Figure , the WAAS is made up of a series of Wide Area Reference Stations, Wide Area Master Stations,
Ground Uplink Stations and Geostationary Satellites (GEOs). The Wide Area Reference Stations, which are
geographically distributed, pick up GPS satellite data and route it to the Wide Area Master Stations where wide area
corrections are generated. These corrections are sent to the Ground Uplink Stations, which up-link them to the GEOs for
re-transmission on the GPS L1 frequency. These GEOs transmit signals which carry accuracy and integrity messages,
and which also provide additional ranging signals for added availability, continuity and accuracy. These GEO signals are
available over a wide area and can be received and processed by ordinary GPS receivers. GPS user receivers are thus
able to receive WAAS data in-band and use not only differential corrections, but also integrity, residual errors and
ionospheric information for each monitored satellite.
The signal broadcast via the WAAS GEOs to the WAAS users is designed to minimize modifications to standard GPS
receivers. As such, the GPS L1 frequency (1575.42 MHz) is used, together with GPS-type modulation - e.g. a
Coarse/Acquisition (C/A) pseudorandom (PRN) code. In addition, the code phase timing is maintained close to GPS time
to provide a ranging capability.


















