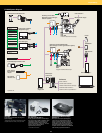
Expandability
Dimensions (mm) Weight (kg) Power consumption
Microscope with scan unit BX61/BX61WI 320 (W) x 580 (D) x 565 (H) 41
—
IX81 350 (W) x 750 (D) x 640 (H) 51
Fluorescence illumination unit Lamp 180 (W) x 320 (D) x 235 (H) 6.7
Power supply 90 (W) x 270 (D) x 180 (H) 3.0 AC 100-240 V 50/60 Hz 1.6 A
Transmitted light detection unit 170 (W) x 330 (D) x 130 (H) 5.9 —
Microscope control unit 125 (W) x 332 (D) x 216 (H) 5.2 AC 100-120/220-240 V 50/60 Hz 3.5 A/1.5 A
FV Power supply unit 180 (W) x 328 (D) x 424 (H) 7.5 AC 100-120/220-240 V 50/60 Hz 4.0 A/2.0 A
FV control unit (PC) 180 (W) x 420 (D) x 360 (H) 10.5 AC 100/240 V 50/60 Hz 497.5 W
19 inch, dual (value per monitor) 363 (W) x 216 (D) x 389.5–489.5 (H) 5.9 AC100-120/200-240 V 50/60 Hz 0.65 A/0.4 A
29.8 inch 689 (W) x 254.7 (D) x 511.5–629.5(H) 15.7 AC100-120/200-240 V 50/60Hz 1.8 A/0.8 A
Power supply unit for laser combiner 210 (W) x 300(D) x 100 (H) 4.0 AC 100-120/200-240 V 50/60 Hz 2.0 A/1.0 A
Laser combiner (with Ar laser heads) 514 (W) x 504 (D) x 236 (H) 45 —
Laser combiner (without Ar laser heads) 514 (W) x 364 (D) x 236 (H) 40 —
LD559 laser power supply 200 (W) x 330 (D) x 52 (H) 1.2 AC 100-240 V 50/60 Hz 30 W
Multi Ar laser power supply 162 (W) x 287 (D) x 91 (H) 4.4 AC 100-240 V 50/60 Hz 20 A
HeNe(G) laser power supply 130 (W) x 224 (D) x 62 (H) 1.8 AC 100-120 V 50/60 Hz 0.45 A
1310
Depth: 990
1200
1880
680
Recommended FV1000 system setup
(IX81, BX61, BX61WI) (unit: mm)
Dimensions, Weight and Power Consumption
Display
*1 This product corresponds to regulated goods as stipulated in the "Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Control Law".
An export license from the Japanese government is required when exporting or leaving Japan with this product.
*2 The performance and safety of this device is not guaranteed if it is disassembled or modified.
*3 This device is designed for use in industrial environments for the EMC performance. (IEC61326-1 Class A device)
Using it in a residential environment may affect other equipment in the environment.
Hippocampal neurons
Courtesy of Dr. Shigeo Okabe
Department of Cellular Neurobiology, Graduate School of
Medicine, The University of Tokyo
Cultured nerve cells derived from the mouse hippocampus
Courtesy of Dr. Koji Ikegami, Dr. Mitsutoshi Setou
Molecular Geriatric Medicine, Mitsubishi Kagaku Institute of Life
Sciences
Cerebellum Purkinje cell
Courtesy of Dr. Tetsuro Kashiwabara, Assistant Professor; and
Dr. Akira Mizoguchi, Professor;
Neuroregenerative medicine course, Mie University School of
Medicine
Drosophila, Stage 14
Courtesy of Dr. Tetsuya Kojima
Laboratory of Innovational Biology, Department of Integrated
Biosciences Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, University
of Tokyo
"Brainbow" mouse brain stem
Courtesy of the laboratories of Jeff W. Lichtman and Joshua R.
Sanes Harvard University MCB Department and the Center for
Brain Science
Mouse brain section
Courtesy of Mr. Masayuki Sekiguchi (Section Chief)
Department of Degenerative Neurological Diseases,
National Institute of Neuroscience, National Center of
Neurology and Psychiatry
Rudimentary limbs of larva in latter part of 3rd instar
Courtesy of Dr. Tetsuya Kojima
Laboratory of Innovational Biology, Department of Integrated
Biosciences, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, University
of Tokyo
Zebrafish
Courtesy of Dr. Toru Murakami,
Department of Neuromuscular & Developmental Anatomy,
Gunma University Graduate School of Medicine
Medaka embryogenesis (somite stage)
Courtesy of Minoru Tanaka, Hiromi Kurokawa
National Institute for Basic Biology Laboratory of Molecular
Genetics for Reproduction
Pilidium larva of Micrura alaskensis
Courtesy of Dr. Svetlana Maslakova of the University of
Washington and Dr. Mikhail V Matz of the Whitney Laboratory
for Marine Bioscience, University of Florida.
Osteoclast induced from rat monocyte in rat kidney
Courtesy of Dr. Keiko Suzuki,
Department of Pharmacology, Showa University School of
Dentistry
Fucci–Sliced mouse brain, expressing S/G2/M phases
Courtesy of Dr. Hiroshi Kurokawa, Ms. Asako Sakaue-Sawano
and Dr. Atsushi Miyawaki
RIKEN Brain Science Institute Laboratory for Cell Function
Dynamics
Immunolabeling of a transgenic mouse retina showing the
major retinal cells types
Courtesy of Dr. Rachel Wong, Mr. Josh Morgan
Dept. Biological Structure, University of Washington, Seattle.
Wild-type embryo in stage 17 of drosophila
Courtesy of Dr. Tetsuya Kojima
Laboratory of Innovational Biology, Department of Integrated
Biosciences
Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, University of Tokyo
Alpha Blend method (Cultured nerve cells derived from the
mouse hippocampus)
Courtesy of Dr. Koji Ikegami, Dr. Mitsutoshi Setou
Molecular Geriatric Medicine, Mitsubishi Kagaku Institute of Life
Sciences
26
Images are courtesy of the following institutions: