Positioning Control Components of Positioning Control and Their Roles 3
3-9
3.3 Drive mechanism
The drive mechanism converts the rotation motion of the servo motor into the reciprocating or
vertical motion through a speed reducer, timing belt, ball screw, etc. to move the machine.
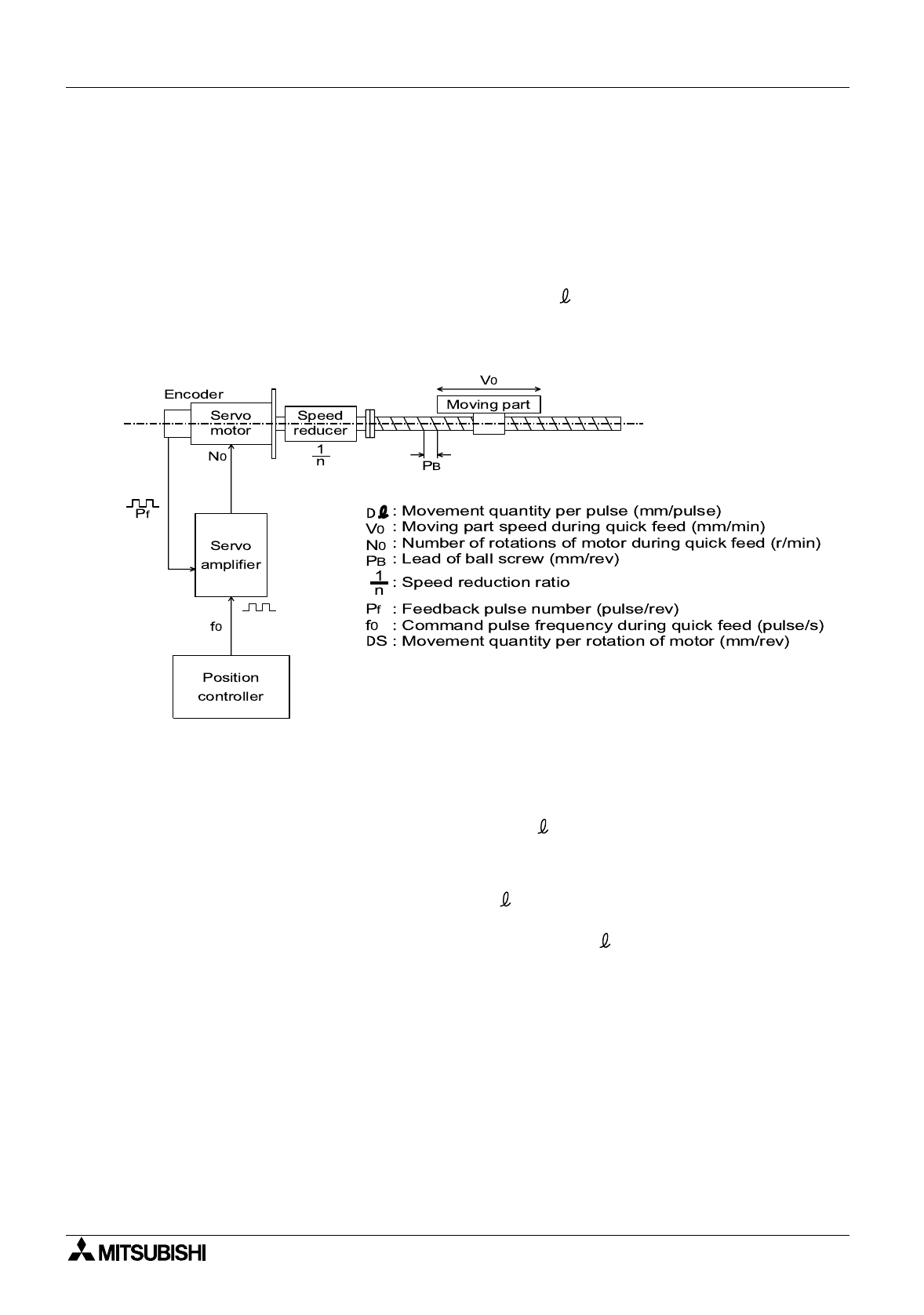
3.3.1 Concept of drive system movement quantity
1) Representative positioning system using AC servo motor
*2 In the structure design, parameters (such as ∆ and V
0
) should be determined in
advance.
a) The servo motor stops with the precision (±∆ ) which is within ±1 pulse against the
command pulse.
b) The movement quantity of the work piece is
"Output pulses from position controller × ∆ ".
The moving part speed is
"Command pulse frequency from position controller × ∆ ".
c) Either "mm", "inch", "degree" or "pulse" can be selected as the positioning command
unit. Accordingly, when data such as the movement quantity per pulse, positioning speed
or the positioning address in accordance with the positioning command unit are set, the
pulse trains calculated inside the positioning controller are output for the target address,
and positioning is performed.


















