Positioning Control The World of Positioning Control 1
1-5
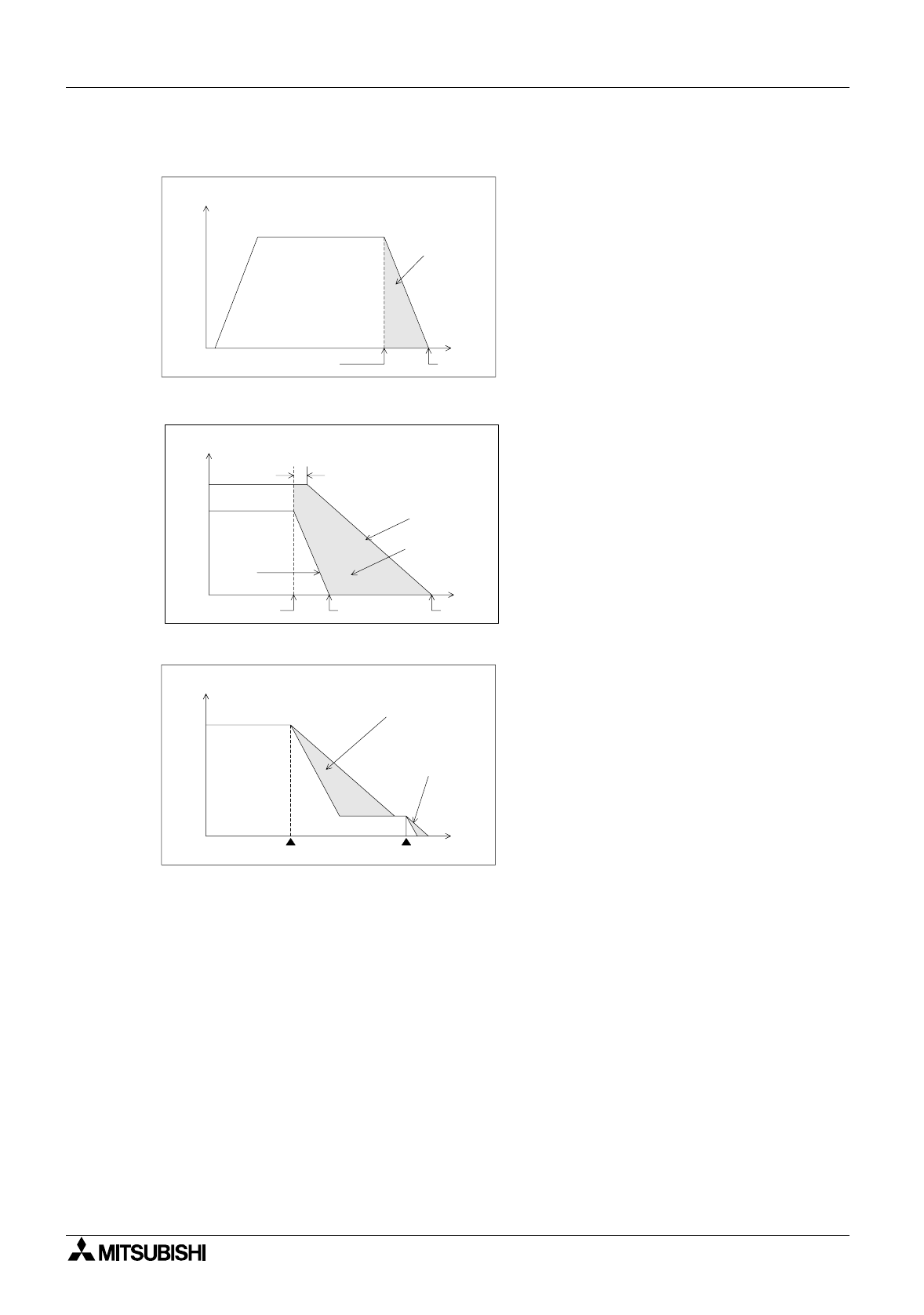
2) Positioning method and stop precision
< Limit switch method >
- When automatically stopping a moving
part driven by a motor, stop the motor by a
position signal, detected by a limit switch
(in general conditions, turn on the brake at
the same time).
- The moving part continues by a coasting
distance until it completely stops, after the
stop command is given. The coasting
distance is shaded in the figure.
- The stop precision is equivalent to the
dispersion in the shaded area as shown in
the figure on the left.
The dispersion is affected by the speed
when the stop command is given, the load
size and the time delay since the stop
command is given, until speed reduction
actually starts.
- If the required stop precision is not
satisfactory when stopping from the
normal operation speed, the most effective
method to improve the stop precision is to
reduce the operation speed.
- However, if the operation speed is simply
reduced, the machine efficiency may also
be reduced. In actual operation, the motor
speed can be reduced from high speed to
low speed once, then the motor stopped.
Velocity
Stop command
Stop
Time
Coasting
distance
Velocity
Stop command
Stop
Time
Light load
Large inertia
Stop
Dispersion
in stop
Heavy
load
Small
inertia
Speed reduction start
Time delay
Velocity
Speed reduction command
Time
Stop command
Dispersion
in stop
High speed
Dispersion in
speed reduction
distance