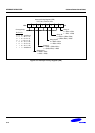
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 INTERRUPT STRUCTURE
5-17
FAST INTERRUPT PROCESSING (Continued)
Two other system registers support fast interrupt processing:
— The instruction pointer (IP) contains the starting address of the service routine (and is later used to swap the
program counter values), and
— When a fast interrupt occurs, the contents of the FLAGS register is stored in an unmapped, dedicated register
called FLAGS' (“FLAGS prime”).
NOTE
For the S3C8245/C8249 microcontroller, the service routine for any one of the eight interrupt levels: IRQ0–
IRQ7, can be selected for fast interrupt processing.
Procedure for Initiating Fast Interrupts
To initiate fast interrupt processing, follow these steps:
1. Load the start address of the service routine into the instruction pointer (IP).
2. Load the interrupt level number (IRQn) into the fast interrupt selection field (SYM.4–SYM.2)
3. Write a "1" to the fast interrupt enable bit in the SYM register.
Fast Interrupt Service Routine
When an interrupt occurs in the level selected for fast interrupt processing, the following events occur:
1. The contents of the instruction pointer and the PC are swapped.
2. The FLAG register values are written to the FLAGS' (“FLAGS prime”) register.
3. The fast interrupt status bit in the FLAGS register is set.
4. The interrupt is serviced.
5. Assuming that the fast interrupt status bit is set, when the fast interrupt service routine ends, the instruction
pointer and PC values are swapped back.
6. The content of FLAGS' (“FLAGS prime”) is copied automatically back to the FLAGS register.
7. The fast interrupt status bit in FLAGS is cleared automatically.
Relationship to Interrupt Pending Bit Types
As described previously, there are two types of interrupt pending bits: One type that is automatically cleared by
hardware after the interrupt service routine is acknowledged and executed; the other that must be cleared by the
application program's interrupt service routine. You can select fast interrupt processing for interrupts with either type
of pending condition clear function — by hardware or by software.
Programming Guidelines
Remember that the only way to enable/disable a fast interrupt is to set/clear the fast interrupt enable bit in the SYM
register, SYM.1. Executing an EI or DI instruction globally enables or disables all interrupt processing, including fast
interrupts. If you use fast interrupts, remember to load the IP with a new start address when the fast interrupt service
routine ends.