Positioning Control Components of Positioning Control and Their Roles 3
3-8
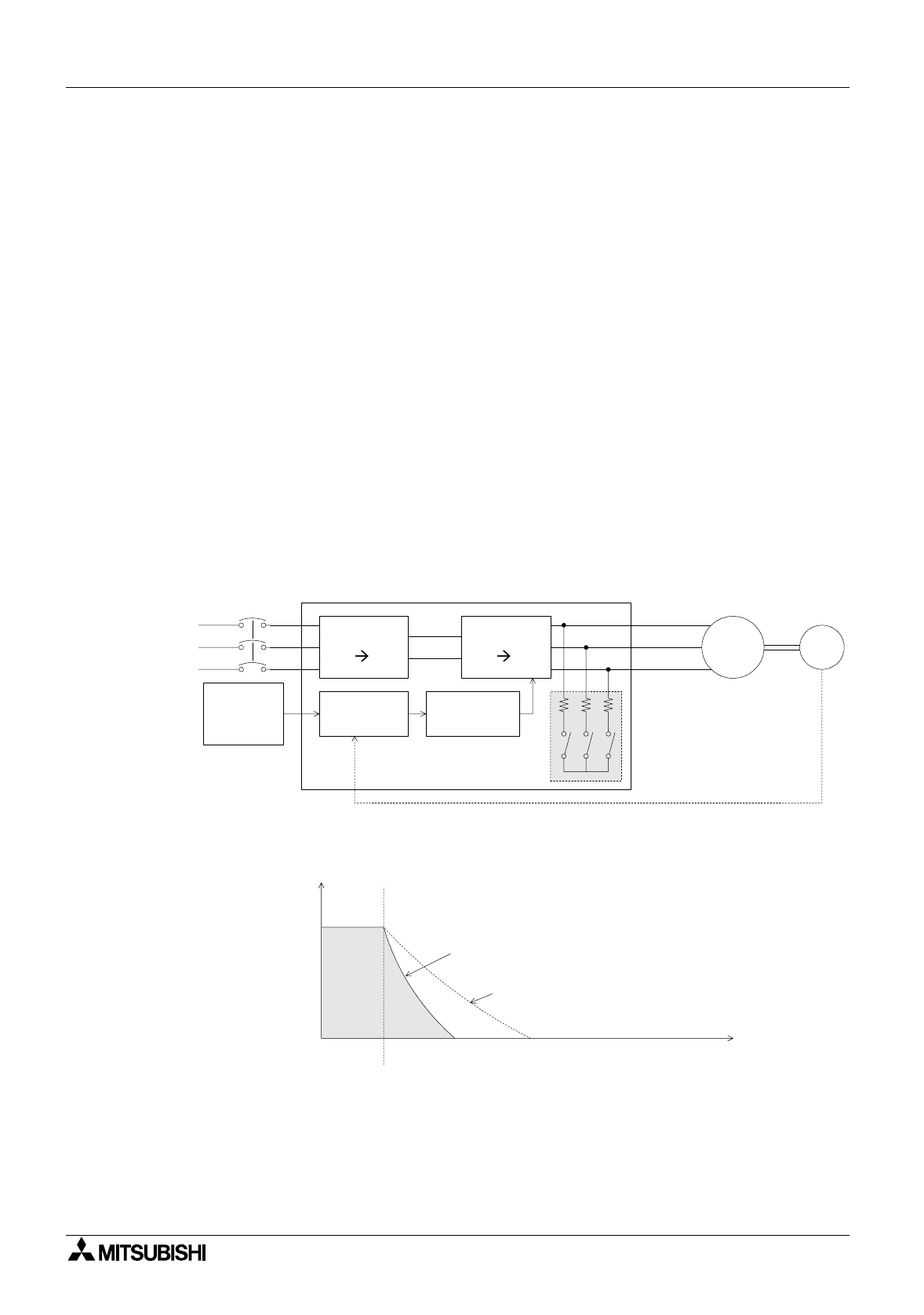
3.2.4 Regenerative brake function
• During deceleration, because the servo motor rotates by the load inertia of the drive
mechanism, it functions as a generator and electric power returns to the servo amplifier.
The regenerative resistor absorbs this electric power, and functions as a brake (called a
regenerative brake.)
• The regenerative brake is required to prevent regenerative over voltage in the servo
amplifier when the load inertia is large and the operation is frequently performed.
• The regenerative resistor is required when the regenerative power generation quantity
during deceleration exceeds the allowable regenerative electric power of the servo
amplifier.
3.2.5 Dynamic brake function
• When a circuit inside the servo amplifier is disabled by a power interruption in the AC power
of the main circuit or actuation of the protective circuit, the terminals of the servo motor are
short-circuited via resistors, the rotation energy is consumed as heat, then the motor
immediately stops without free run.
• When the motor stops by elimination of the rotation energy, the brake is not effective and
the motor runs freely.
Power: OFF
Contacts of dynamic brake: ON
Motor stop characteristics when the
dynamic brake is actuated
Number of
rotations of motor
Time
When the dynamic brake
is not actuated
Converter
AC DC
S
R
T
NFB
Deviation
counter
D/A
conversion
Position
controller
Main
circuit
AC power
supply
V
U
W
These contacts of the
dynamic brake turn ON
when the power is
interrupted.
SM PLG
Inverter
DC AC


















