Positioning Control The World of Positioning Control 1
1-4
1.3 Positioning method type
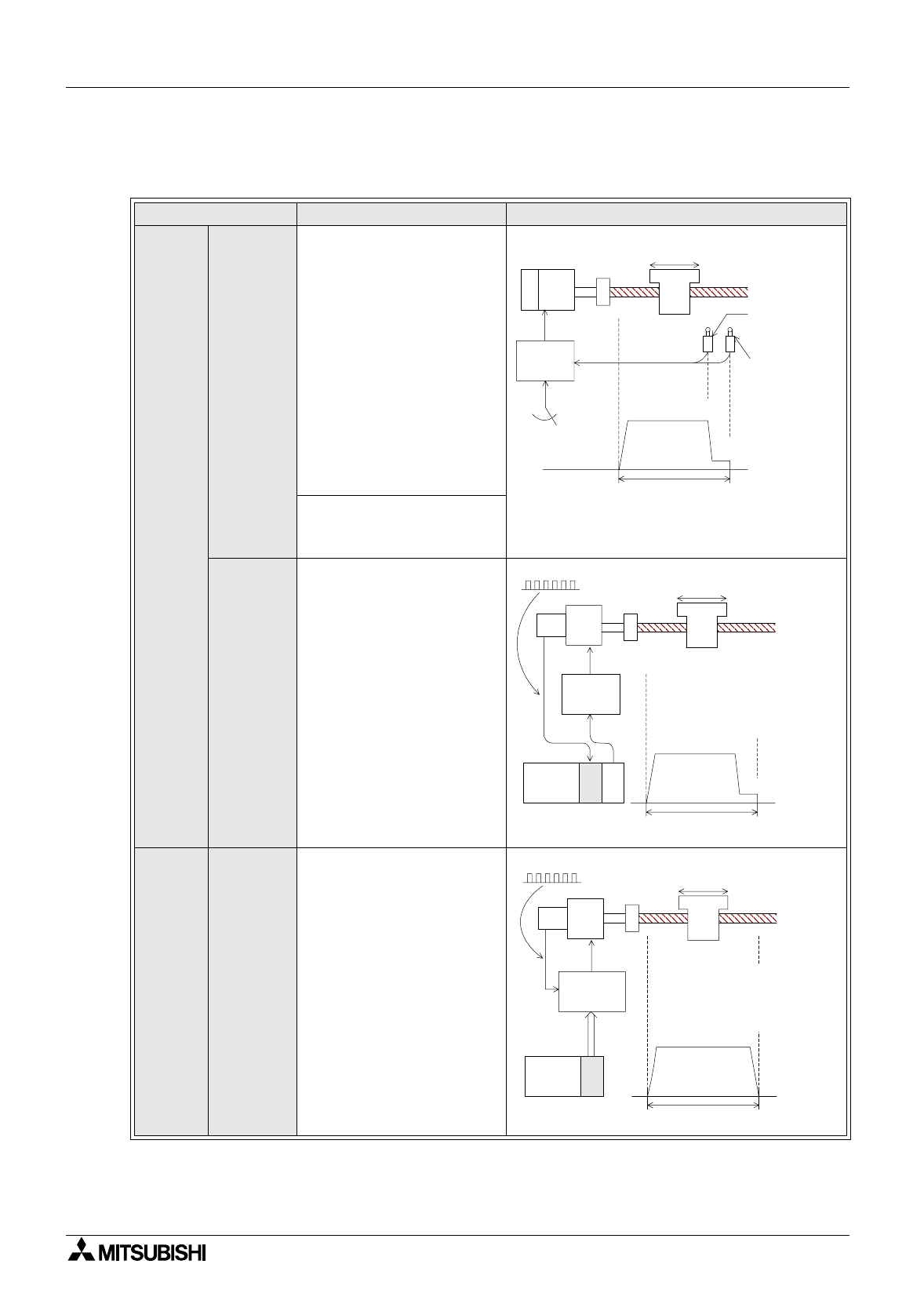
1) There are three types of positioning method
*1 The stop precision shows a value in a case where low speed is 10 to 100 mm/s.
Control method Description Schematic drawing
Speed
control
Limit
switch
method
Two limit switches are
provided in places where a
systems moving part
passes. At the first limit
switch, the motor speed is
reduced. At the second limit
switch, the motor turns off
and the brake turns on, to
stop the moving part.
In this method, because
position controllers are not
required, the system
configuration can be realized
at reasonable cost.
(Guideline of stopping
precision: Approximately
±1.0 to 5.0 mm)*
Pulse
count
method
A position detector (such as
pulse encoder) is set up in a
motor or rotation axis. The
pulse number generated
from the position detector is
counted by a high-speed
counter. When the pulse
number reaches the preset
value, the moving part stops.
In this method, because limit
switches are not used, the
stop position can be easily
changed.
Position
control
Pulse
command
method
An AC servo motor which
rotates in proportion to the
input pulse number is used
as the drive motor.
When the pulse number
corresponding to the
movement distance is input
to the servo amplifier of the
AC servo motor, positioning
can be performed at high
speed in proportion to the
pulse frequency.
B IM
INV
DC0 to 10V
High speed
Low speed
Limit switch for
changeover to
low speed
Limit switch
for stop
Ball screw
IM: Inductive motor
B: Brake
INV: Inverter
Moving part
Movement
distance
PLG
High speed
Low speed
Ball screw
IM: Inductive motor
PLG: Pulse generator
INV: Inverter
PLC: Programmable controller
Moving part
Movement distance
PC
High-speed
counter unit
DC0 to
10V
Pulses are
fed back.
IM
INV
PLG SM
Servo
amplifier
Ball screw
SM: Servo motor
PLG: Pulse generator
PLC: Programmable
controller
Moving part
Movement distance
PC
Position controller
Pulses are
fed back.
Command
pulse