Philips Semiconductors
User’s Manual - Preliminary -
P89LPC901/902/903
CLOCKS
2003 Dec 8 32
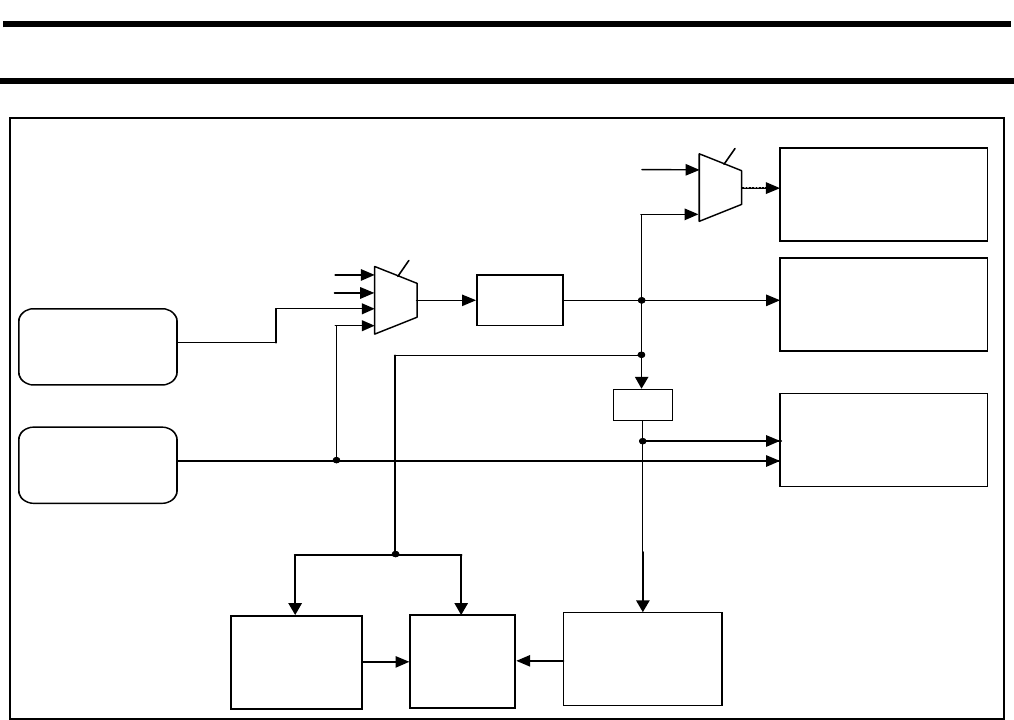
Figure 2-5: Block Diagram of Oscillator Control- P89LPC903
CPU Clock (CCLK) Wakeup Delay
The P89LPC901/902/903 has an internal wakeup timer that delays the clock until it stabilizes depending to the clock source used.
If the clock source is any of the three crystal selections (P89LPC901), the delay is 992 OSCCLK cycles plus 60-100µs. If the
clock source is either the internal RC oscillator or the Watchdog oscillator, the delay is 224 OSCCLK cycles plus 60-100µs.
CPU Clock (CCLK) Modification: DIVM Register
The OSCCLK frequency can be divided down, by an integer, up to 510 times by configuring a dividing register, DIVM, to provide
CCLK. This produces the CCLK frequency using the following formula:
CCLK frequency = f
OSC
/ (2N)
Where: f
OSC
is the frequency of OSCCLK
N is the value of DIVM.
Since N ranges from 0 to 255, the CCLK frequency can be in the range of f
OSC
to f
OSC
/510 (for N =0, CCLK = f
OSC
) .
This feature makes it possible to temporarily run the CPU at a lower rate, reducing power consumption. By dividing the clock, the
CPU can retain the ability to respond to events other than those that can cause interrupts (i.e. events that allow exiting the Idle
mode) by executing its normal program at a lower rate. This can often result in lower power consumption than in Idle mode. This
can allow bypassing the oscillator start-up time in cases where Power down mode would otherwise be used. The value of DIVM
may be changed by the program at any time without interrupting code execution.
RTC
CPU
Watchdog
Oscillator
RC Oscillator
/2
DIVM
WDT
(7.3728MHz)
(400KHz)
CCLK
UART
Timer 0 & 1
PCLK
CPU
Clock
Baud rate
Generator
RTCS1:0
OSC
CLK
FOSC2:0