18
Non-Invasive Blood Pressure (NIBP) Measurement
Non-Invasive Pressure Measurement Principles
Oscillometric method
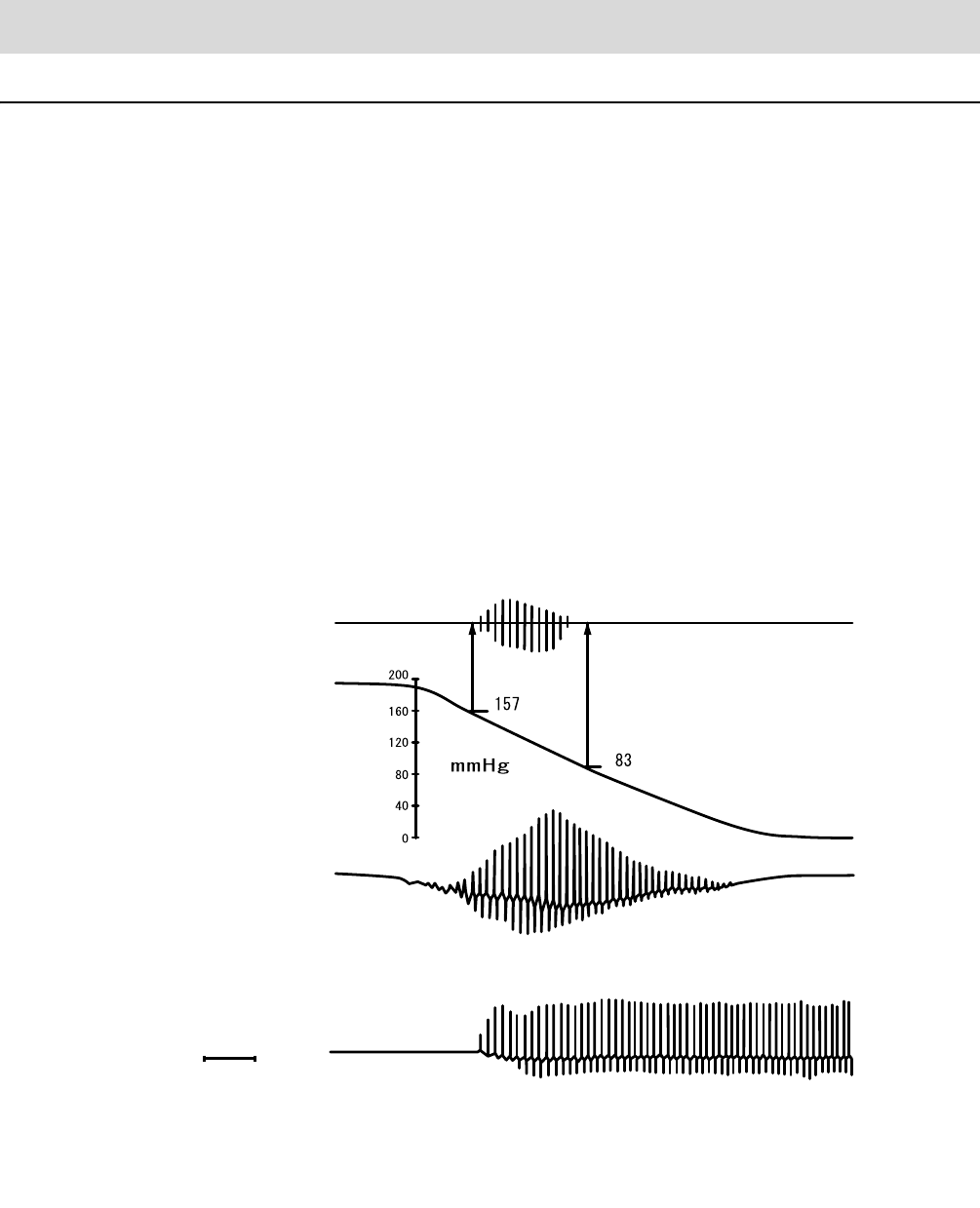
The beat in the pulsation generated by the contraction of the heart is captured as the pressure inside
the cuff to measure the blood pressure. If the cuff wrapped around the upper arm is pressurized
sufficiently, the blood flow stops, but the beat of the pulsation is present and the pressure inside the cuff
receives this and oscillates. Next, as the pressure inside the cuff gradually decreases, the oscillation of
the pressure within the cuff gradually increases and reaches a peak. As the pressure within the cuff
decreases further, the oscillation decreases from its peak.
The pressure within the cuff and the relationship with the increase and decrease of the oscillation within
the cuff in this series of processes are stored into memory, calculations are carried out, and the blood
pressure value is determined.
The pressure within the cuff when the oscillation increases drastically is the systolic pressure and the
pressure within the cuff when the oscillation decreases drastically is the diastolic pressure. Also, the
pressure within the cuff when the oscillation peaks is taken as the average pulsation pressure.
The oscillometric method does not determine the blood pressure value instantly like a microphone type
automatic blood pressure gauge with the auscultation method, but rather determines it from the series
of change curves as explained above. Therefore, it is not easily affected by external noise, an electric
scalpel or other electro surgical instruments.
KOROTKOV SOUNDS
RADIAL PULSE
5 SEC
OSCILLATIONS IN CUFF PRESSURE
CUFF
PRESSURE
Comparison between the auscultatory, oscillometric and
palpatory methods of measuring blood pressure.
L.A. Geddes,
“The Direct and Indirect Measurement of Blood Pressure”, Year Book Medical Publishers, Inc. 1970
