2-3
Teledyne Analytical Instruments
Model OT-2 System Operational Theory 2
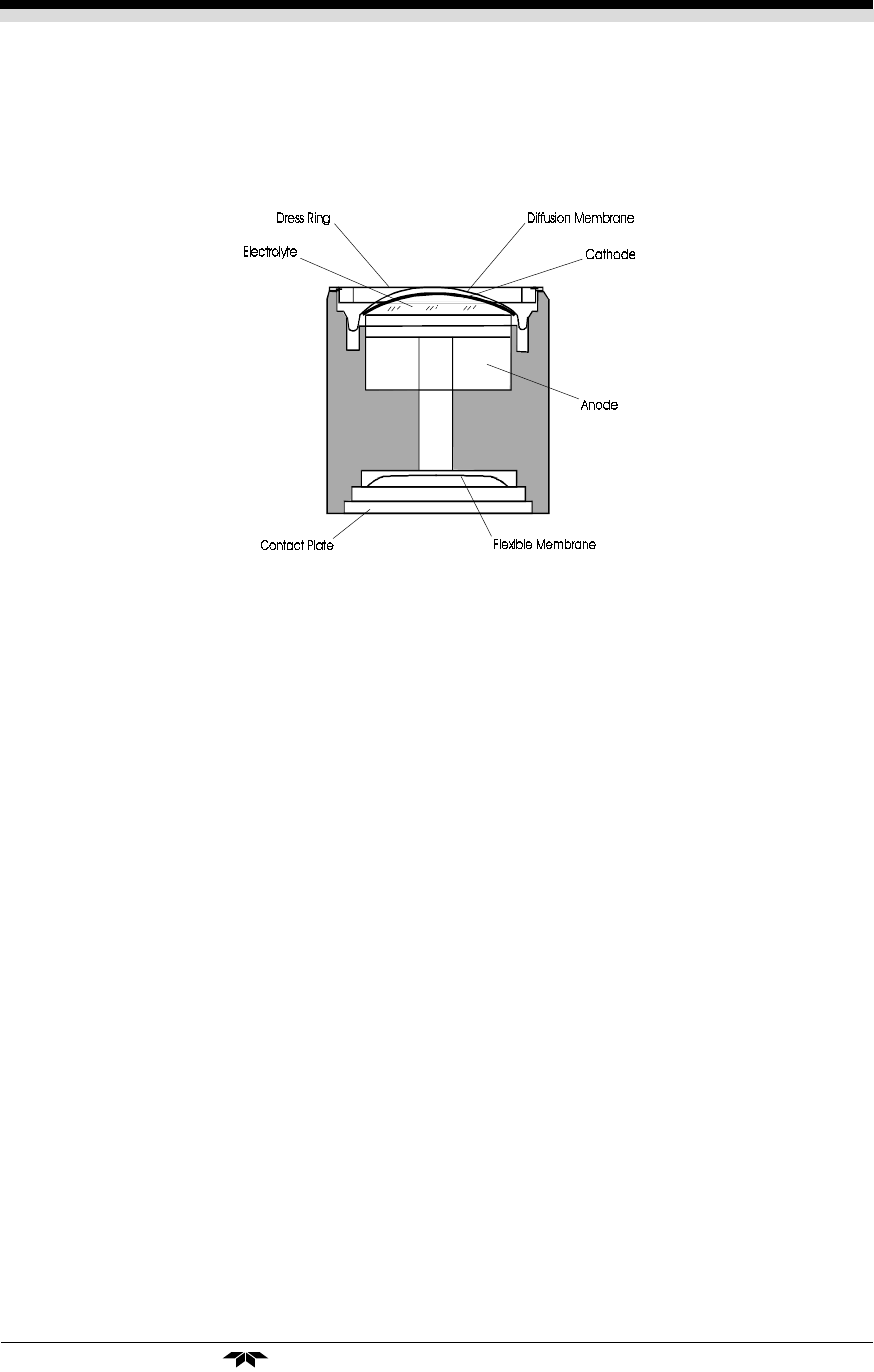
Refer to Figure 2-2,
Cross Section of a Micro-Fuel Cell
, which
illustrates the following internal description.
Figure 2-2. Cross Section of a Micro-Fuel Cell (not to scale)
At the top end of the cell is a diffusion membrane of Teflon.
Beneath the diffusion membrane lies the oxygen sensing ele-
ment—the cathode.
The anode provides the electrical driving force for the reduc-
tion of oxygen at the cathode.
At the rear of the cell, just below the anode structure, is a
flexible membrane designed to accommodate the internal vol-
ume changes that occur throughout the life of the cell. This flexibil-
ity assures that the sensing membrane remains in its proper posi-
tion, keeping the electrical output constant.
The entire space between the diffusion membrane, above the
cathode, and the flexible rear membrane, beneath the anode, is
filled with electrolyte. Cathode and anode are submerged in this
common pool. They each have a conductor connecting them to
one of the external contact rings on the contact plate, which is on
the bottom of the cell.