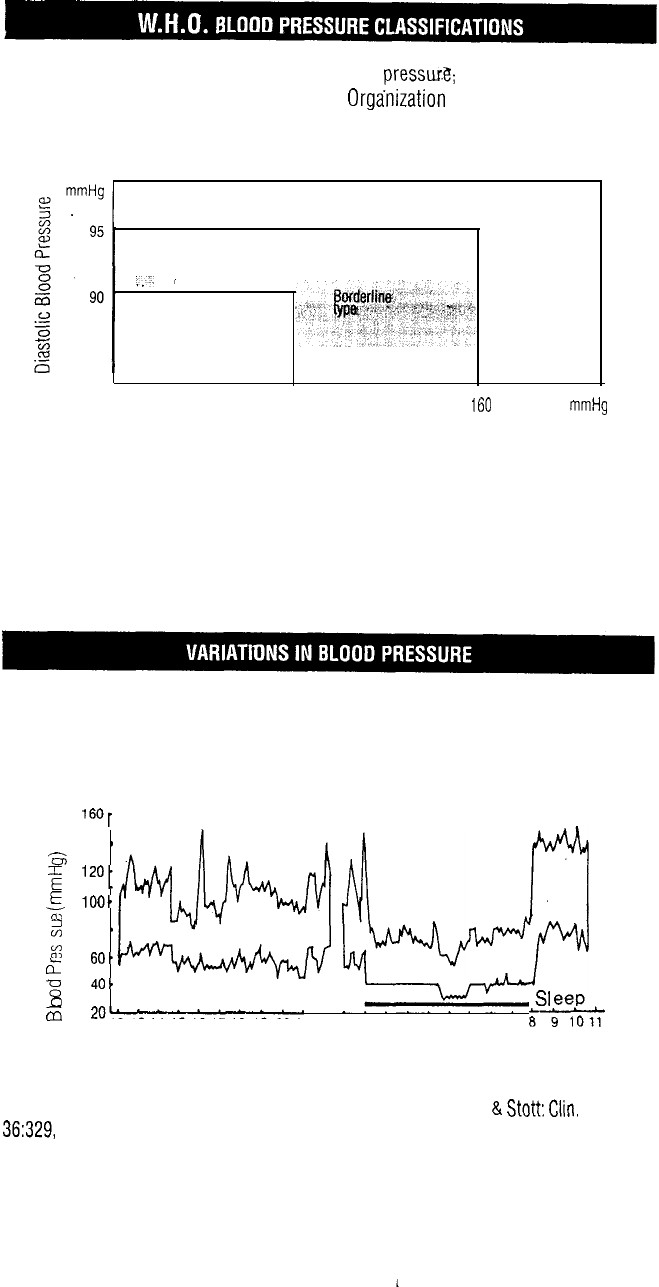
Standards for assessment of high or low blood pressur.$ without regard to age,
have been established by the World Health Orga’nization (WHO), as shown in this
chart.
(Fig. 1)
..‘.
(
Normal blood
pressure type
Hypertense
pressure type
140
160 mmHg
Reference Material: Investigation into Adult Diseases Report by the Ministry of Health
and Social Security, 1971.
Individual blood pressures vary greatly both on a daily and a seasonal basis.
These variations are even more pronounced in hypertense patients. Normally the
blood pressure rises while at work and is at its lowest during the sleeping
period. The graph below illustrates the variations in blood pressure over a whole
day with measurement taken every five minutes.
1601
A
B
(Fig. 2)
140
*
Gi
E
lZO.
E
100,
22
2
80
*
z
CT
60.
g
40.
0
m
20d’...““.
&
SI
eep
12
131415161718
19
2021
22 23 24
1
2 3 4 5 6 7
69
PM
Time
AM
Shown is data tor measurements taken every 5 minutes. The thick line represents sleep.
The rise in blood pressure at 4 PM (A in the graph) and 12 PM (B in the graph) corre-
spond to an attack of pain and sexual intercourse. (Beven, Honour
&
Stott:
Clin.
Sci.
36:329,
1969.)














