1413
Recalling Stored Data
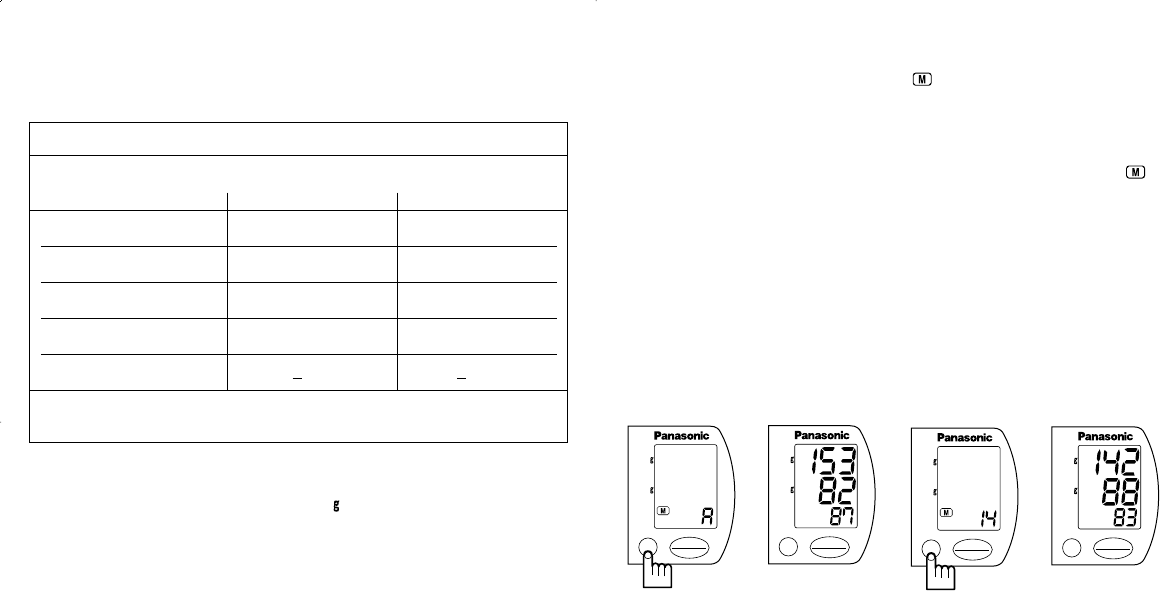
1. Press the Recall button (Fig. 13). The A will appear in the lower part of
the display, and then the average value of all the stored data will be
displayed (Fig. 14).
• For example, if seven data (measurements) are stored in the memory,
the average value of these seven data will be displayed. If there is no
data in the memory or if there is only one data in the memory, the A
will not be displayed.
2. By pressing the Recall button repeatedly (Fig. 15), you can browse through
all the stored data sequentially from the newest data to the oldest (Fig. 16).
• If no data is in the memory, nothing will be displayed.
Note:
Press the Recall button lightly and briefly. If the Recall button is pressed
continuously for more than about 2 seconds, all stored data will be deleted.
3. Press the Start (On/Off) button to finish.
• If the data is recalled while the blood pressure monitor is turned off, the
monitor will turn off automatically after about 30 seconds.
Fig. 13 Fig. 14 Fig. 15 Fig. 16
Deleting Data
1. Press the Recall button.
2. Press the Recall button again until the recalled data disappears from the
display (about 2 seconds).
• ALL data will be deleted. Individual stored data cannot be deleted
independently.
R
On/Off
Start
SYS.
mmH
DIA.
mmH
P/
min.
R
On/Off
Start
SYS.
mmH
DIA.
mmH
P/
min.
R
On/Off
Start
SYS.
mmH
DIA.
mmH
P/
min.
R
On/Off
Start
SYS.
mmH
DIA.
mmH
P/
min.
IMPORTANT:
• WHO does not define a low blood pressure area. For reference, systolic
pressure readings of less than 90 mmH are considered to indicate low
blood pressure regardless of the diastolic pressure.
• Do not be alarmed by temporarily high or low readings because fluctuations
in a person’s blood pressure are not uncommon. If possible, measure and
record your blood pressure at the same time every day, and consult your
physician if you have questions or concerns.
• If abnormal variations in blood pressure are observed in measurement,
please consult your physician.
Easily Check Your Blood Pressure Readings
Against the World Health Organization (WHO)
Guidelines
Blood Pressure Categories
If your systolic pressure falls in one category but your diastolic pressure
in another, your level is classified in the higher of the two categories.
CATEGORY
Normal
Normal High
Low Hypertensive
Moderate Hypertensive
Severe Hypertensive
SYSTOLIC BLOOD
PRESSURE (SBP)
< 130
130-139
140-159
160-179
> 180
DIASTOLIC BLOOD
PRESSURE (DBP)
< 85
85-89
90-99
100-109
> 110


















