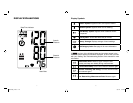
5 6
This table is applicable to most adults aged 18 and older.
Blood pressure tends to go up and down, even in people
who normally don’t have high readings. If your numbers
stay above the “normal” range most of the time, you may
be at increased risk and should consult your physician.
Although one can easily find where their own blood
pressure readings fall on this table, this monitor comes
equipped with a Risk Category Index that automatically
compares each reading to this criteria and provides a
helpful cue if your reading falls into one of the stages that
could potentially indicate increased risk. See page 21 for
more information on this feature.
Please note that cues provided by this monitor are only
intended to assist you in using this table. The table and
cues are only provided for convenience to have access to
the NIH information. They are not a substitute for a medical
examination by your physician. It is important for you to
consult with your physician regularly. Your physician will tell
you your normal blood pressure range as well as the point
at which you may actually be considered to be at risk.
ABOUT BLOOD PRESSURE
What is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the pressure exerted on the artery
walls while blood flows through the arteries. The pressure
measured when the heart contracts and sends blood
out of the heart is systolic (highest) blood pressure. The
pressure measured when the heart dilates with blood
flowing back into the heart is called diastolic (lowest)
blood pressure.
Why Measure Your Blood Pressure?
Among today’s various health problems, those associated
with high blood pressure are very common. High blood
pressure dangerously correlates with cardiovascular
diseases. Therefore, blood pressure monitoring is
important for identifying those at risk.
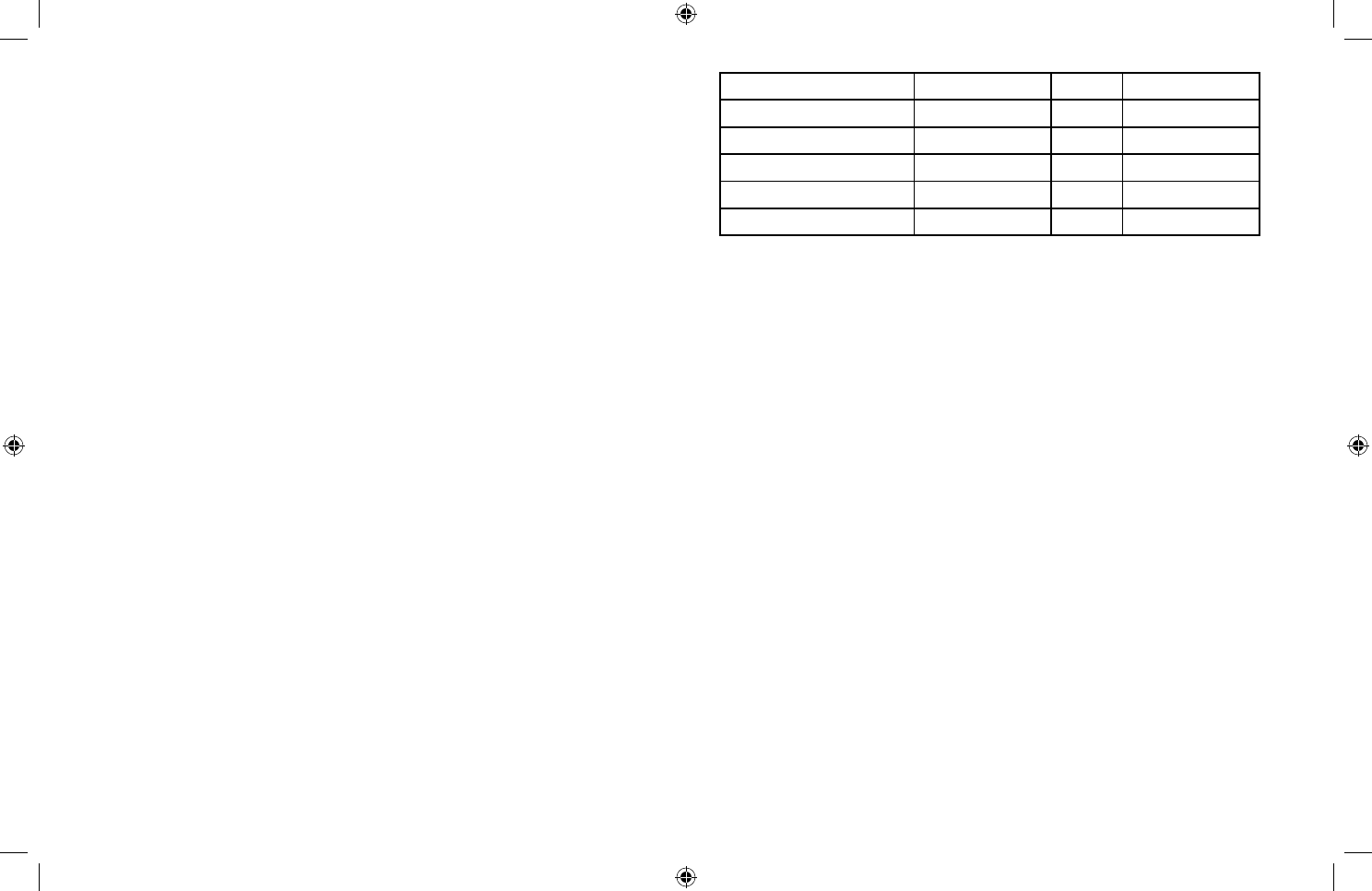
BLOOD PRESSURE STANDARD
The table on page 6 is criteria for hypertension that is
publicly available from the National Heart Lung and Blood
Institute at the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH)
(http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Diseases/Hbp/HBP_WhatIs.html). Users
can compare their own blood pressure readings against
these established criteria to determine if they may be
potentially at increased risk.
Category
Systolic (mmHg) Diastolic (mmHg)
Normal Less than 120 and Less than 80
Prehypertension 120-139 or 80-89
High Blood Pressure
Stage 1 140-159 or 90-99
Stage 2 160 or higher or 100 or higher
BPS-060_B.indd 7-8BPS-060_B.indd 7-8 5/01/10 1:27 PM5/01/10 1:27 PM