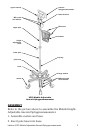
Labtron V223 Mobile Adjustable Aneroid Sphygmomanometer 5
are written with the highest value rst, then the lowest
value. Readings of 120/80 are considered to be normal,
with high blood pressure being dened as a systolic
pressure which is 140mmHg or more at rest and a diastolic
pressure which is 90mmHg or more at rest. Only a patient’s
physician is qualied to determine whether the readings
obtained are normal for that person.
Measuring blood pressure: Have the patient, while relaxed
and in a sitting position, extend the arm from which the
blood pressure will be taken to the front or laterally with
the palm of the hand up.
Attach the cuff and diaphragm: Hold the end of the cuff
containing the ination bag rmly against the inside of the
bare upper arm with the artery symbol positioned over the
brachial artery. Never place the cuff over clothing. Pull
the opposite end of the cuff snugly around the arm and
secure the hook and loop fastener strips. The range lines,
indicated by the arrows, show the correct cuff size when
the cuff is placed on the arm. If the index line on the end
of the cuff falls between the two range lines, the cuff is the
proper size. If the index line falls outside the range lines, a
larger or smaller cuff should be used. The cuff should be
snug, but not too tight. If one or two ngers can t between
the cuff and the arm, the cuff is properly secured. Place
the diaphragm of the stethoscope over the brachial artery
inferior to the cuff.
Inflating the cuff: Close the bulb’s air valve by turning the
air release valve clockwise. Squeeze the ination bulb at a
steady rate until the gauge’s needle points at approximately
30mmHg above the individual’s normal systolic pressure
value. If the individual’s normal blood pressure is not
known, it is recommended to inate to 200mmHg.
Systolic blood pressure reading: Open the air release
valve slowly by turning it counter-clockwise while holding
the diaphragm of the stethoscope over the brachial artery.