English
9
General information about blood pressure
The blood circulation is responsible for supplying the body with oxygen. Blood
pressure is the pressure exerted on the arteries when the blood flows through
them.
The higher blood pressure value (= systolic pressure or top value) signifies the
blood pressure produced by contraction of the heart muscle and subsequent
pumping of blood into the arterial system.
The lower blood pressure value (= diastolic pressure or lower value) repre-
sents the blood pressure produced by the relaxation phase of the heart
muscle, during which blood flows back into the heart.
* There is no universally accepted definition of hypotension. However, those
having the systolic pressure below 100 mmHg are assumed to have hypoten
sion.
Health and blood pressure
The incidence of hypertension increases with age. In addition, a lack of exer-
cise, excess body fat and high levels of cholesterol (LDL) which sticks to the in-
side to blood vessels, reduces elasticity of these vessels. Hypertension accele-
rates arterial sclerosis, which can lead to very serious conditions such as stroke
and myocardial infarction. For these reasons it is very important to know
whether our blood pressure is within a healthy range. Blood pressure fluctuates
from minute to minute, throughout the day. Therefore it is essential to take
regular readings to help identify an average blood pressure for you.
Classification of Blood Pressure by the World health
Organization
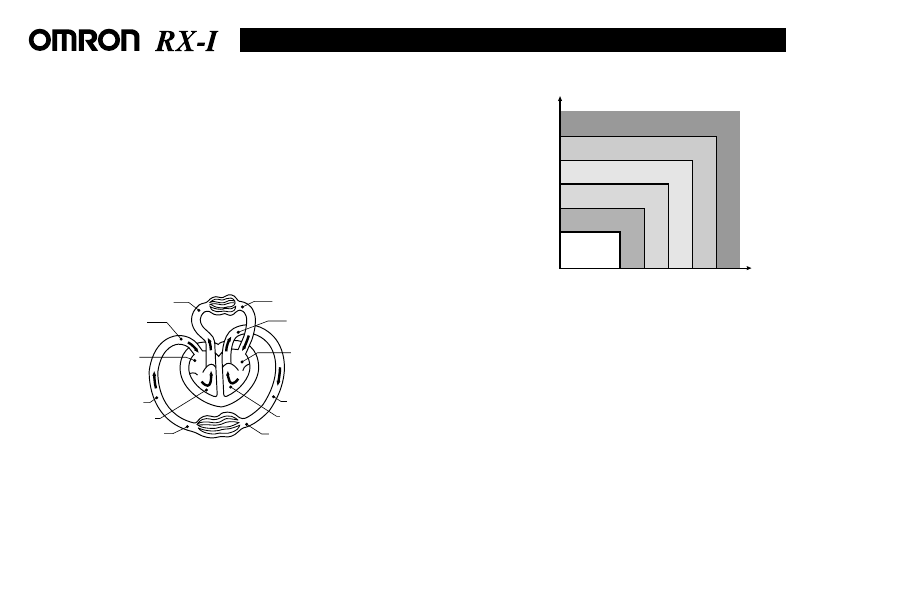
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Society of
Hypertension (ISH) developed the blood pressure classification shown in
the Figure. (This classification is based on the blood pressure values
measured by sitting on a chair in the outpatient department of a hospital.)
Optimal blood
pressure
(target value)
Normal blood
pressure
Normal systolic value
Mild hypertension
Moderate hypertension
Severe hypertension
80 85
90 100 110
120
130
140
160
180
Systolic blood pressure
(mmHg)
Diastolic
blood
pressure
(mmHg)
According to the blood pressure classification by the WHO/ISH* (revised in 1999)
* ISH: International Society of Hypertension
Pulmonary (lung)
capillaries
Pulmonary veinPulmonary artery
Aorta
Left atrium
Arteries
Left ventricle
Arterioles
Body capillaries
Vena cava
Right atrium
Veins
Right ventricle
Venules











