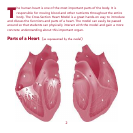
A. Superior Vena Cava – A large vein that carries oxygen poor blood into the
heart from the upper body and into the right atrium.
B. Right Atrium – Blood from the vena cava enters into the right atrium and is
then sent to the right ventricle.
C. Inferior Vena Cava – A large vein that carries oxygen poor blood into the
heart from the lower body and into the right atrium.
D. Tricuspid Valve – The valve separating the right atrium and right ventricle,
preventing blood from flowing in the wrong direction.
E. Right Ventricle – Collects blood from the right atrium and then pumps it
through the pulmonary valve.
F. Pulmonary Valve – A valve that is between the right ventricle and
pulmonary artery.
G. Pulmonary Artery – Carries blood from the heart directly to the lungs. It is also
the only artery that carries oxygen-poor blood.
H. Left Atrium – Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs travel through the body and
into heart through the left atrium.
I. Mitral Valve – The valve separating the left atrium and left ventricle,
preventing blood from flowing in the wrong direction.
J. Left Ventricle – Collects blood from the left atrium and then pumps it through
the entire body except the lungs. The left ventricle is stronger than the right
ventricle since its pumps the blood through the entire body as opposed to just
the lungs.
K. Aortic Valve – The valve that lies between the left ventricle and aorta,
preventing the blood from flowing in the wrong direction.
L. Aorta – Carries the oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to the entire
body, except the lungs. The aorta is also the largest artery in the body.