FLIRTG165USERGUIDEDocumentIdentifier:TG165‐en‐US_AA
28
12Appendices
12.1EmissivityFactorsforCommonMaterials
12.2InfraredEnergyandImagingOverview
Athermalimagergeneratesanimagebasedontemperaturedifferences.Inathermalimagethehottestitemin
thesceneappearsaswhiteandthecoldestitemasblack,andallotheritemsarerepresentedasagrayscale
valuebetweenwhiteandblack.
Itmaytakesometimetoget
usedtothethermalimagery.Havingabasicunderstandingofthedifferences
betweenthermalanddaylightcamerascanhelpwithgettingthebestperformancefromtheTG165.
Onedifferencebetweenthermalanddaylightcamerashastodowithwheretheenergycomesfromtocreatean
image.Whenviewingan
imagewithanordinarycamera,therehastobesomesourceofvisiblelight(something
hot,suchasthesunorlights)thatreflectsoffoftheobjectsinthescenetothecamera.Thesameistruewith
humaneyesight;thevastmajorityofwhatpeopleseeisbasedon
reflectedlightenergy.Ontheotherhand,the
thermalimagerdetectsenergythatisdirectlyradiatedfromobjectsinthescene.
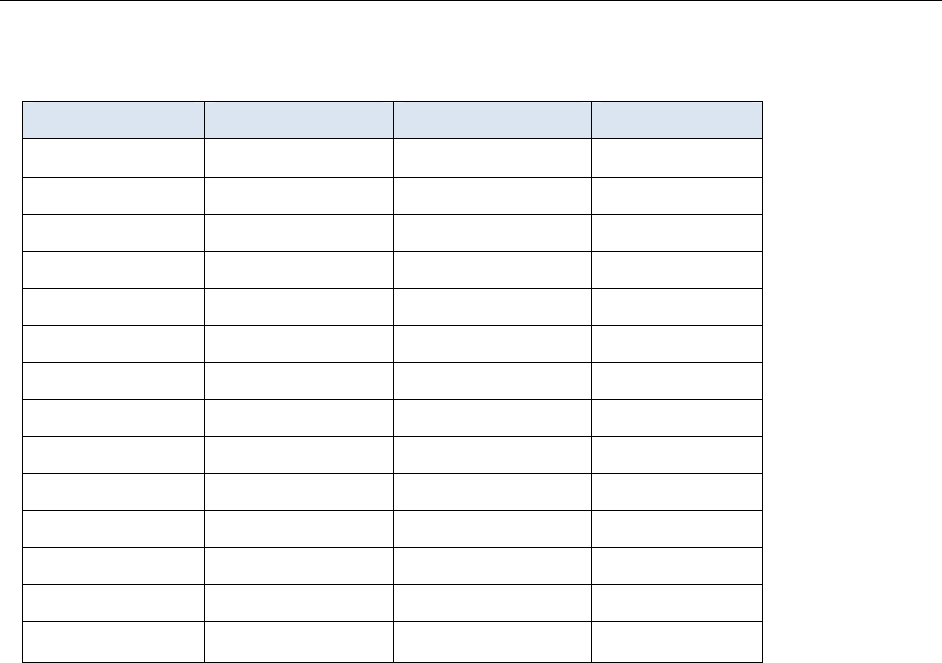
Material Emissivity Material Emissivity
Asphalt 0.90to0.98 Cloth(black) 0.98
Concrete 0.94 Skin(human) 0.98
Cement 0.96 Leather 0.75to0.80
Sand 0.90 Charcoal(powder) 0.96
Soil 0.92to0.96 Lacquer 0.80to0.95
Water 0.92to0.96 Lacquer(matt) 0.97
Ice 0.96to0.98 Rubber(black) 0.94
Snow 0.83 Plastic 0.85to0.95
Glass 0.90to0.95 Timber 0.90
Ceramic 0.90to0.94 Paper 0.70to0.94
Marble 0.94 ChromiumOxides 0.81
Plaster 0.80to0.90 CopperOxides 0.78
Mortar 0.89to0.91 IronOxides 0.78to0.82
Brick 0.93to0.96 Textiles 0.90


















